The idea of orbital mirrors to shine sunlight down onto the night side of Earth precede WWII; Hermann Oberth proposed such at thing in 1923. Today if someone were to seriously propose an orbiting space mirror the probably use would be to *shade* the Earth from sunlight in order to reduce insolation and very, very slightly cool the planet. Still, it might prove an interesting mathematical study… if an orbiting mirror is used to alternately shade the Earth and then light up the Earth, is it a net positive? When you factor in that the night-time sunlight beamed down would presumably offset artificially generated lighting – say, by lighting up a city, replacing streetlights – it may be that the result would be to reduce planetary temperature.
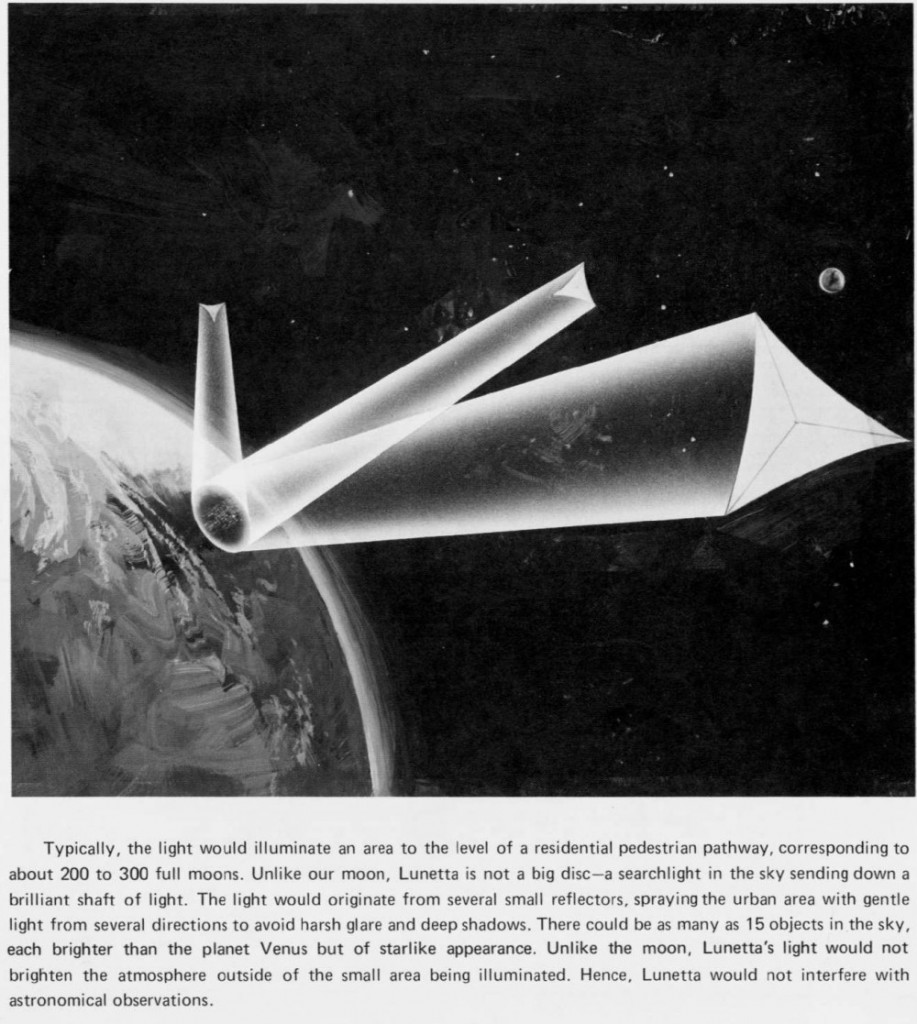
As recently as 1977, Rockwell International (after Krafft Ehricke) examined the use of orbiting mirrors called “Lunetta” to provide illumination.