USSP #04
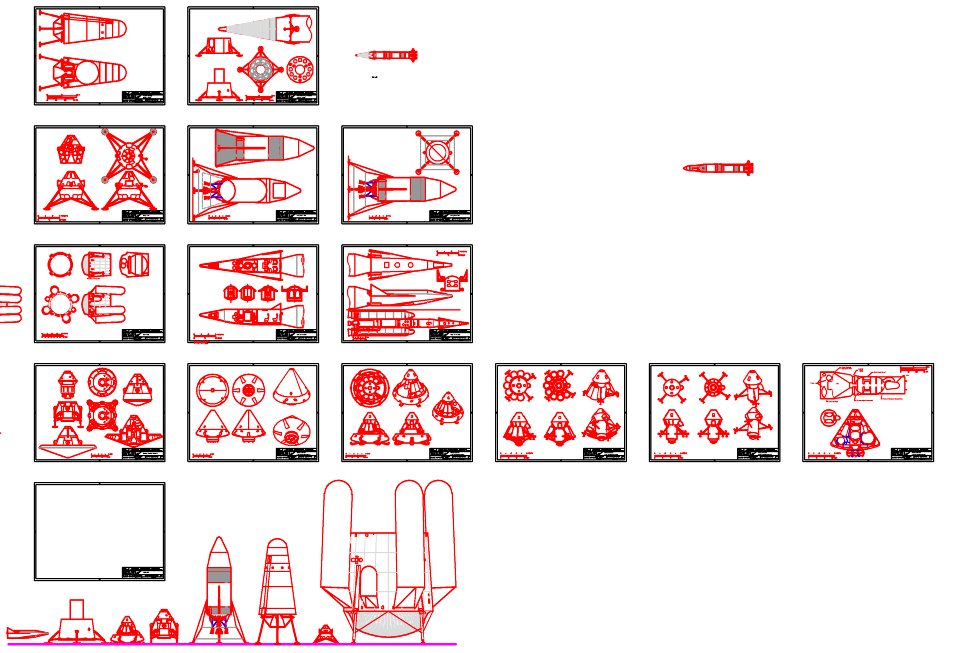
US Spacecraft Projects #04, the Lander Special is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #04 includes:
- GE Electrically Propelled Cargo Vehicle: A lunar lander with a nuclear reactor and ion engines to reduce the cost of lunar logistics
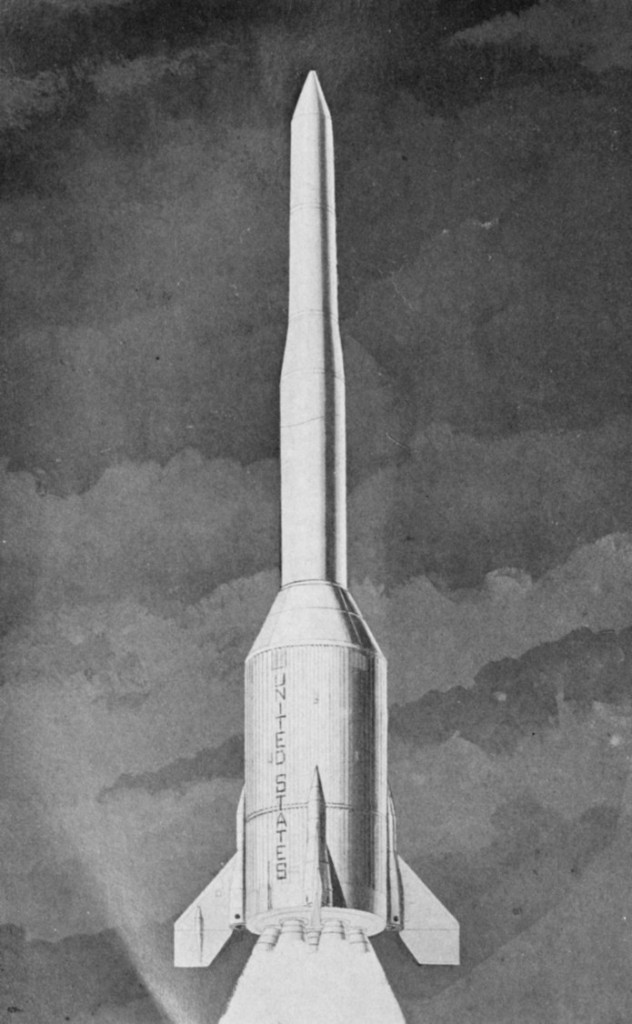
- Douglas LASS: Landing an S-IVb stage on the moon
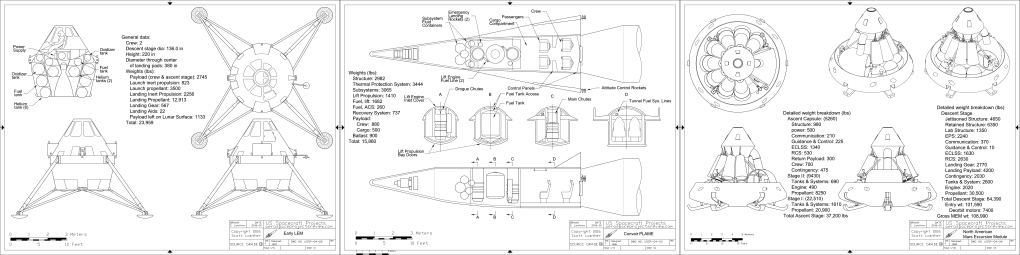
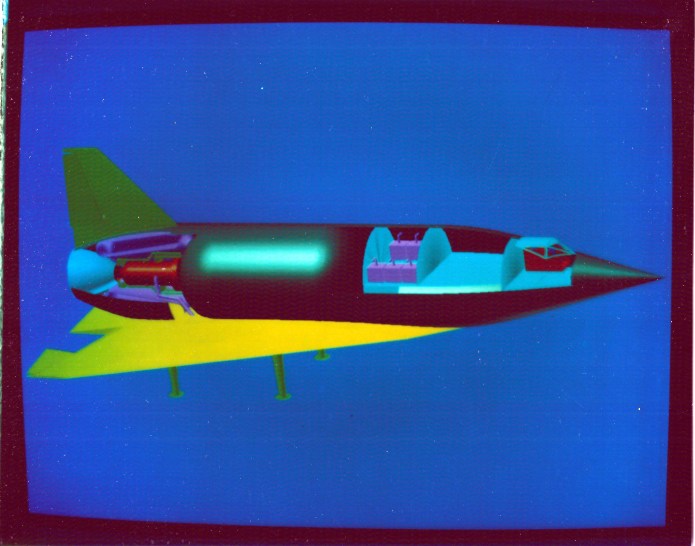
- Convair PLAME: VTOL crew return with jet engines
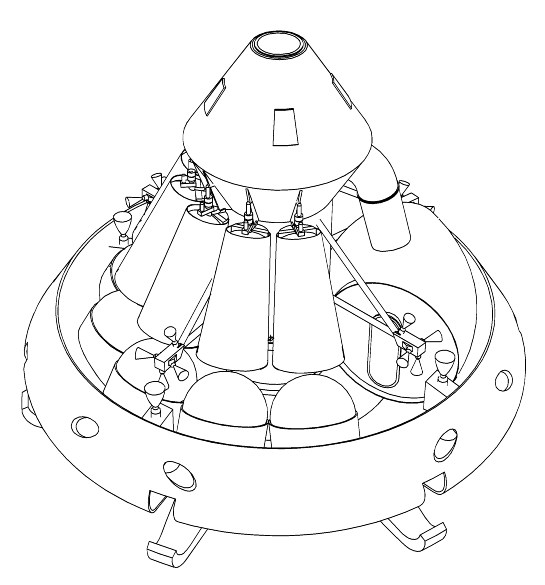
- North American Mars Excursion Module: the iconic conical Mars lander
- Martin-Marietta Ballistic NIMF: A nuclear “hopper”
- Early LEM: One of the first recognizable designs, by Maxime Faget
- ROMBUS: probably the largest lunar lander seriously proposed
- Boeing Lander Module 2: A recent Mars crew lander
USSP #04 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $5:
——–
—–
USTP #05
US Transport Projects #05 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #05 includes:
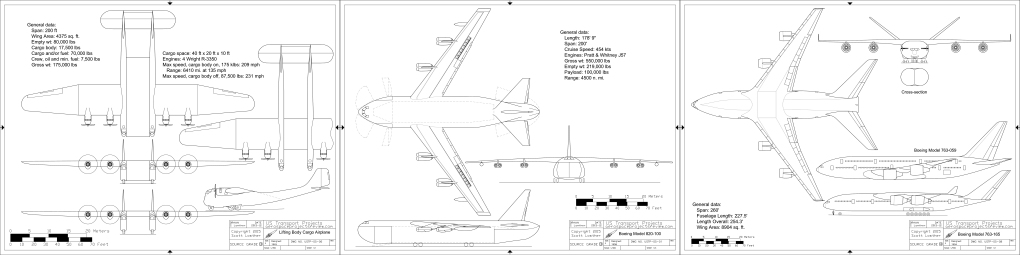
- Boeing Model 820-100: The B-52 can haul more than bombs…
- Lockheed Nuclear Tug: Want to tow two C-5s across an ocean?
- Martin Super Ocean Transport: A WWII-era design for a post-war giant passenger transport
- HOT EAGLE: 13 Marines to Benghazi in minutes
- Sikorsky SST: An early supersonic transport concept
- Lifting Body Cargo Airplane: A wartime design for a multibody design with a separate cargo module
- Resource Air Carrier: A giant “flying pipeline” to haul petroleum
- Boeing Model 763-165: A side-by-side New Large Airplane design
USTP #05 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4:
——–
—–