In 1985, Rockwell International contemplated the business case for Shuttle Derived Launch Vehicles. The specific design illustrated used the ET and SRB’s more or less stock, but the orbiter was replaced with a recoverable propulsion and avionics module. The payload came in the form of an upper stage with something very like the Apollo Command and Service Modules. This would probably have been for a lunar mission of some kind as a Shuttle-class booster is too big for a simple capsule mission to LEO. The basic design would have roughly performed like the presumably forthcoming SLS.
Search Results : shuttle
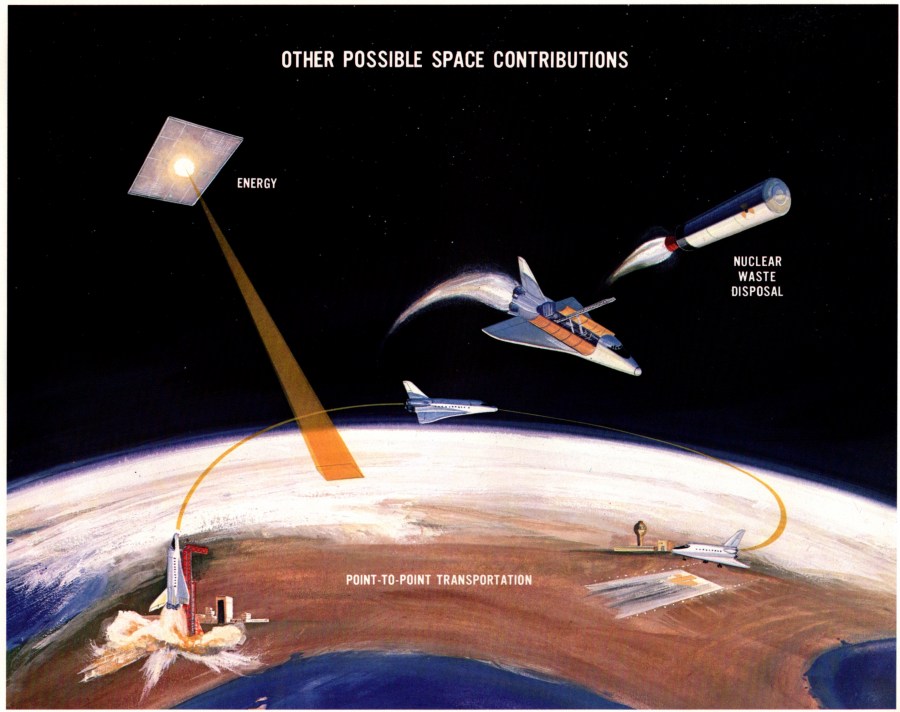
Sometime around 1973/74, NASA put out a report on future aeronautics and space opportunities. While lean on technical detail, and devoid of diagrams (bah), it did have some vaguely interesting 1970’s-style art. The painting below illustrates some of the “other” things that the forthcoming Space Shuttle could do, like launch solar power satellites, lob nuclear waste into deep space and be used for point-to-point Terrestrial passenger transport. Yeah, about that…
Here’s an article from “Future Life” magazine, May 1979, describing a Rockwell concept for a passenger module for the Shuttle. This could carry 74 passengers, a loadout that seems perhaps excessive until you realize that it was meant to transport the crews who would build the miles-long solar power satellites. If this concept is of interest, be sure to check out US Bomber Projects #06, the Solar Power Satellite Launch Special. There, another concept for a Shuttle “bus” was described and illustrated.
Continuing…
In 1985, the Space Shuttle program was already about a decade and a half old, the shuttles themselves were already starting to show themselves as “old tech.” It was clear that they would need replacing with a next generation of vehicle, and of course Rockwell wanted to build whatever “Shuttle II” came along… if for no other reason, a Shuttle II would make the Shuttle instantly obsolete and wipe out Rockwell’s Shuttle-based income. It was obvious that such a system would enter service sometime after the year 2000. Not, of course, very long after 2000. That would be nuts.
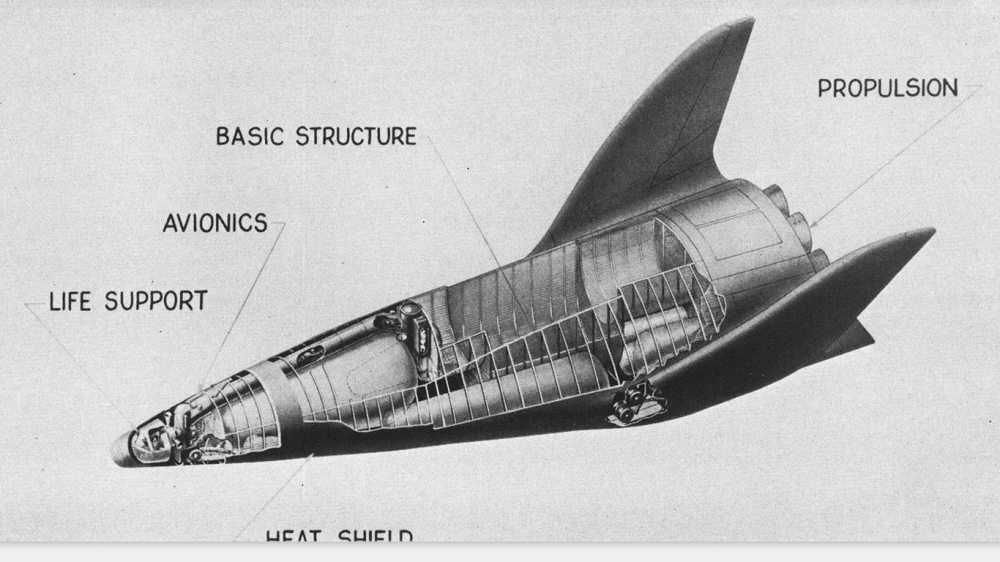
Interestingly, the illustration Rockwell used for the Next Generation Shuttle was not a Rockwell design, but a NASA-Langley concept for a small “Orbit-on-Demand” vehicle. If you’d like more information on this exact design, boy, have I got a deal for you: it was described and illustrated in US Launch Vehicles Projects #03.
For much of the time while the concept of the Space Shuttle was being developed the vehicle consisted of a manned flyback booster of relatively enormous dimensions, coupled with an orbiter that included sizable internal oxygen tanks, sometimes with external hydrogen tanks, sometimes internal. The model below, a masterpiece of late 1960’s model makers craft, illustrates one such concept. the orbiter is similar to the Grumman H-33 except larger, with completely internal hydrogen and oxygen tanks.
Had this type of Space Shuttle been built and flown successfully, there is every chance that it would have been substantially less costly to operate than the Shuttle we got: flying the booster back to a runway landing and refurbishing it would theoretically have been a lot faster and easier than fishing solid rocket motor casings out of the ocean and shipping them to Utah for refurb. But getting the design to the point of operation would have been a nightmare. The booster was unlike anything previously attempted, and would have been an aircraft roughly the size of the C-5 Galaxy, with a top speed like that of the X-15
I have uploaded the full resolution scan of the photo to the 2019-07 APR Extras Dropbox folder, available to $4 and up subscribers to the APR Monthly Historical Documents Program.
A video where some guys get into the archives of the US Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama. On display is a sizable (looks like about 1/50 scale) Space Shuttle, ET and Boosters made from plexiglas. It is a thing of beauty, surely a chore and a half for the model shop back in the day. This is *not* the final Shuttle design; some differences are obvious such as the split cargo bay doors and, while unmentioned in the video, the existence of extended OMS pod fairings, reaching out onto the aft of the cargo bay doors.
Last time I visited the USS&RC in something like 2005 they had a much bigger plexiglas STS model on public display, something like 1/10 scale, along with a gigantic plexiglas Saturn V. Such things are fantastic artifacts, and if you are working on a complex engineering project like this a see-through plexiglass large scale model is terribly helpful. I suspect that such things are only rarely made these days, as computer graphics are a lot easier, cheaper and more readily updatable. But nothing beats a Real Thing. And at least so far, 3D printing is not up to the job of stamping out large-scale transparent models like this. But someday…
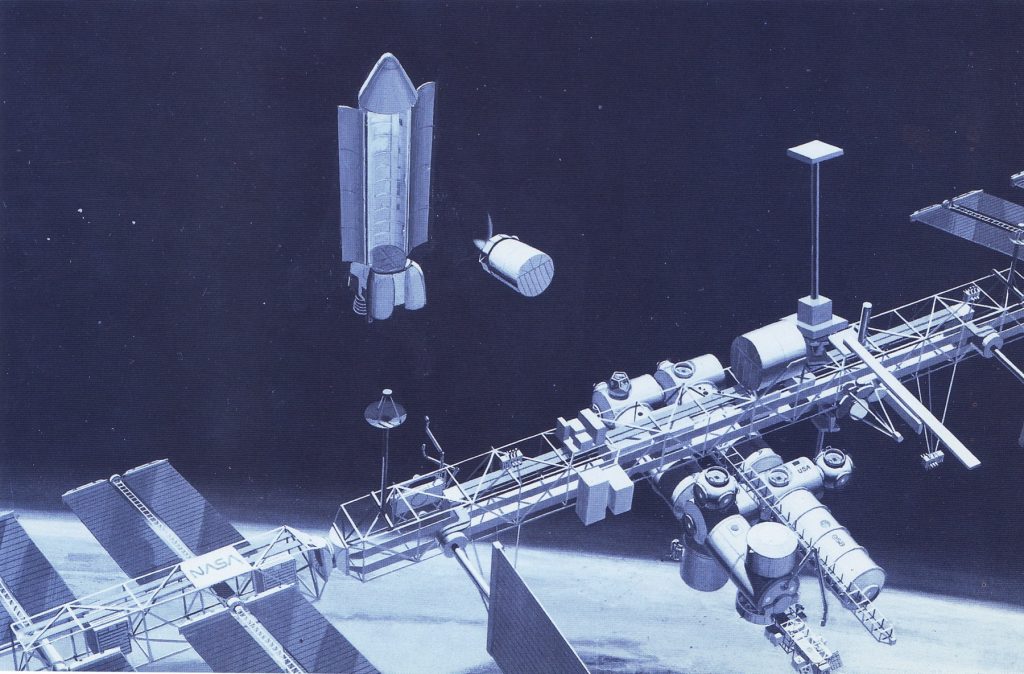
The Shuttle-C of the late 80’s/early 90’s would have carried a whole lot more to orbit than the Shuttle Orbiter, but would not have been quite as capable of precise maneuvering as the Orbiter. Consequently, it might get close to a space station, but it would be unlikely to dock with it unless it was moved into position with secondary orbital maneuvering vehicles or grabbed with manipulator arms. This artwork depicts a Shuttle-C standing off some distance from a space station, with the cargo being shuttled over with an OMV.
The Shuttle-C was described and illustrated in US Launch Vehicle Projects #4.
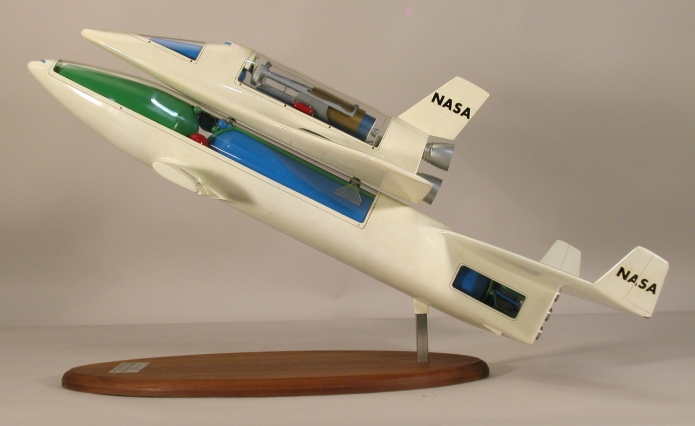
A design circa 1970 for a Lockheed lifting body space shuttle concept. This design was derived from the earlier STAR Clipper stage-and-a-half design from the late 1960s… the whole story of the STAR Clipper and its many derivatives is given in Aerospace Projects Review issue V3N2, available HERE.
Note that this vehicle is equipped with sizable internal propellant tanks. As a result the cockpit is separated from the payload bay; in order to access the payload, the crew would need to pass through a long, narrow tunnel not unlike that within the B-36 bomber.
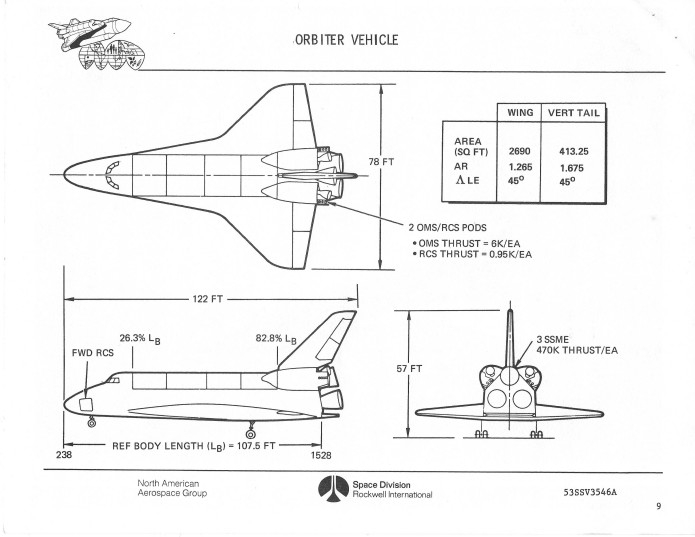
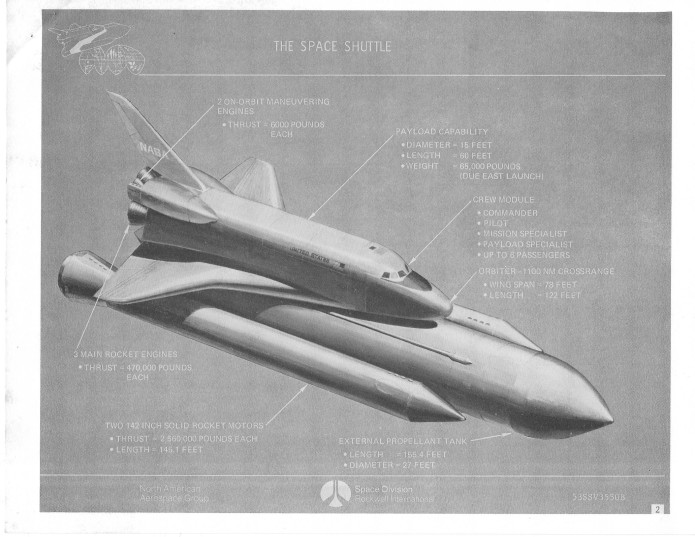
In June 1973 Rockwell put together a short course – presumably or employees new to the STS program – that described the Space Shuttle system as it was then designed. There were a number of clear differences between the STS of the time and the STS as actually built. Differences included a forward extension of the OMS pods, continuing well onto the cargo bay doors. Also, the forward RCS thrusters on the sides of the nose were contained behind sizable doors to protect them during re-entry, a protection that was found to be unnecessary. There were also important differences with the SRBs and ETs.
I have made the full-rez scan of the document available to $10+ APR Patreon patrons. If this sort of thing is of interest, please consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
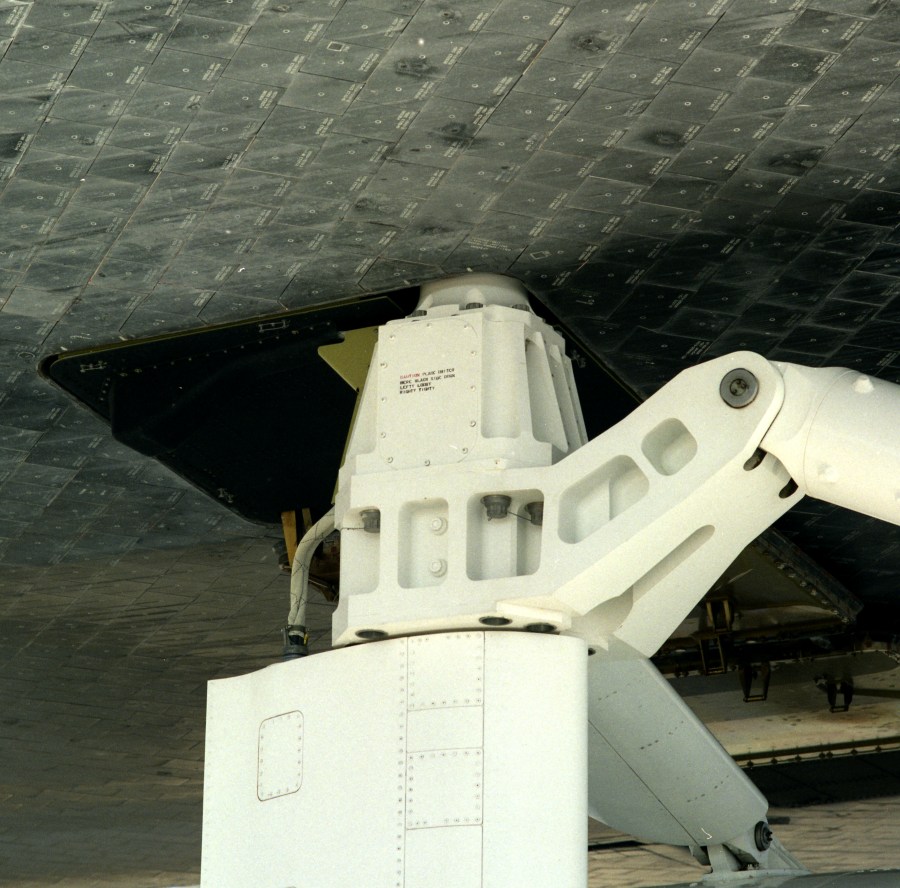
The Shuttle Carrier Aircraft had a trio of posts that connected directly to the underside of the Space Shuttle Orbiter. Unsurprisingly, early on someone with a sense of humor stenciled jokes on them; surprisingly, NASA not only allowed those jokes to remain, but touched them up over the years.
Photos courtesy Dennis R. Jenkins, author of “Space Shuttle: Developing an Icon 1972-2013.” Anyone interested in the Shuttle program *really* should invest in this three-volume masterpiece: