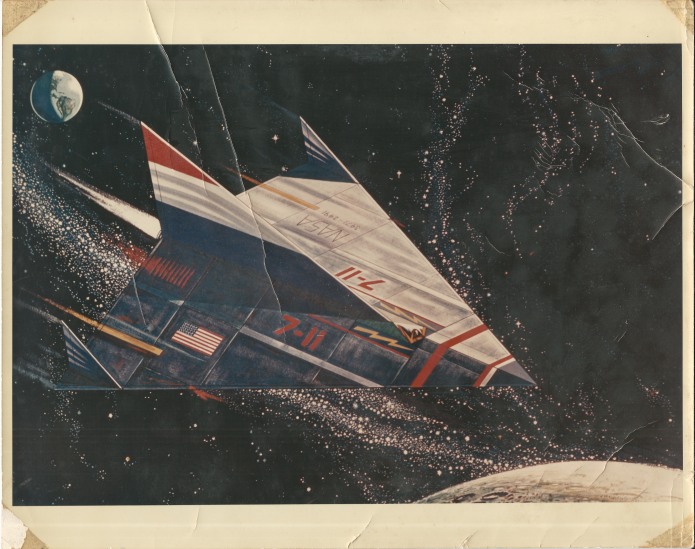
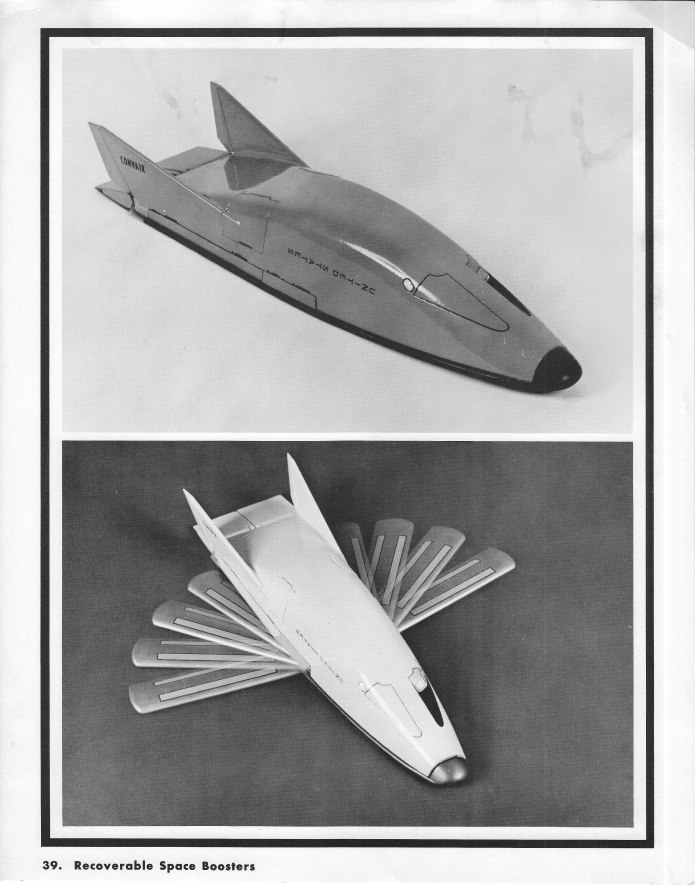
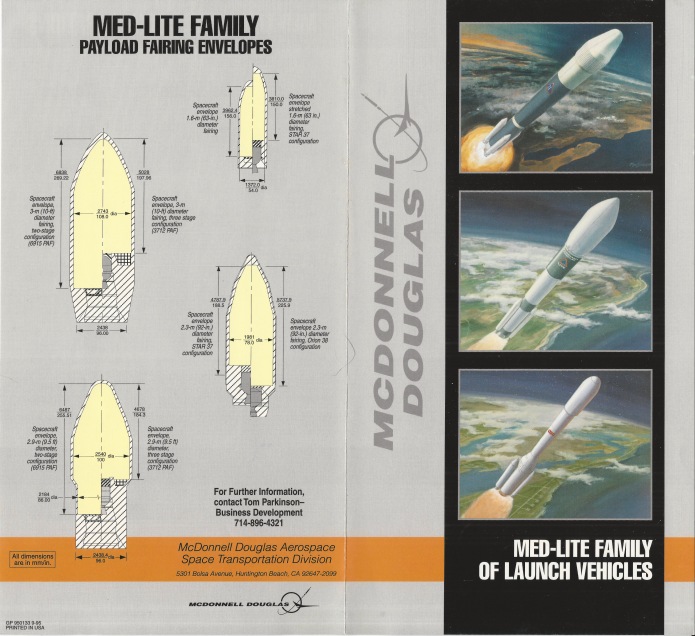
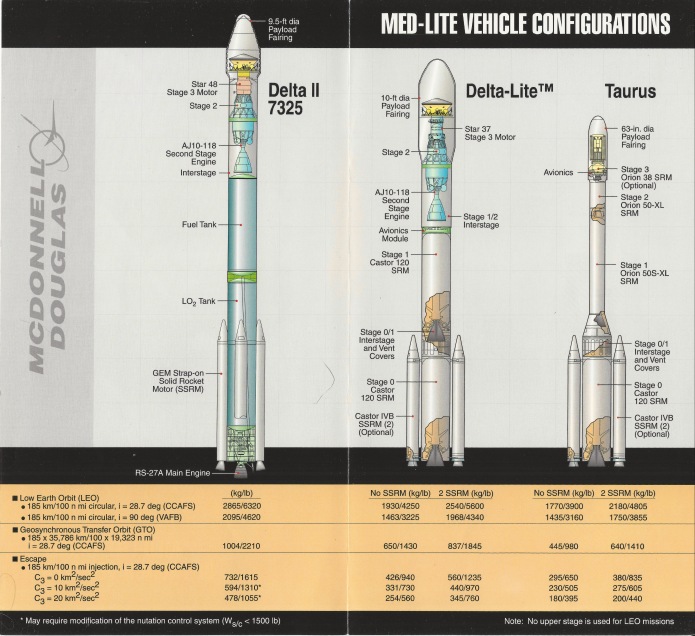
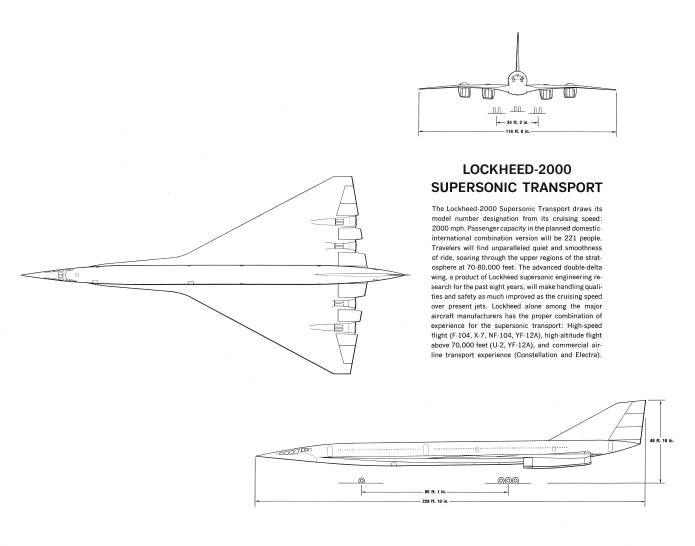
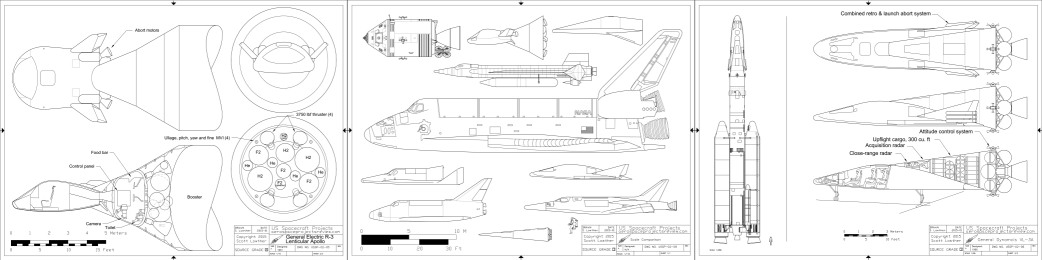
The Convair VL-3A was a 1966 concept for a space station logistics spacecraft. It was a sleek, flat-bottomed lifting body featuring a twin tail and flip-out wings that would deploy shortly before landing to reduce the landing speed. It would be fitted with flip-out turbofan engines for range extension, self-ferry and control during landing. General Dynamics released sizable “educational” cards with information and photos of models of the spaceplane showing how the wings would deploy from within the lower fuselage.
I have uploaded righ-rez scans of both sides of this poster-sized card to the 2018-05 APR Extras folder on Dropbox for APR Patrons at the $4 level and up.
I also wrote about and illustrated the VL-3A in US Spacecraft Projects #2, showing the general arrangement of the design along with the disposable propulsion stage and the launch configuration atop the Titan III.
USSP #02 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $6:
If you are interested in thes VL-3A model images and a great many other “extras” and monthly aerospace history rewards, please sign up for the APR Patreon. What else are you going to spend $4 a month on?