The Hawaii Emergency Management Agency just sent out a helpful text message:
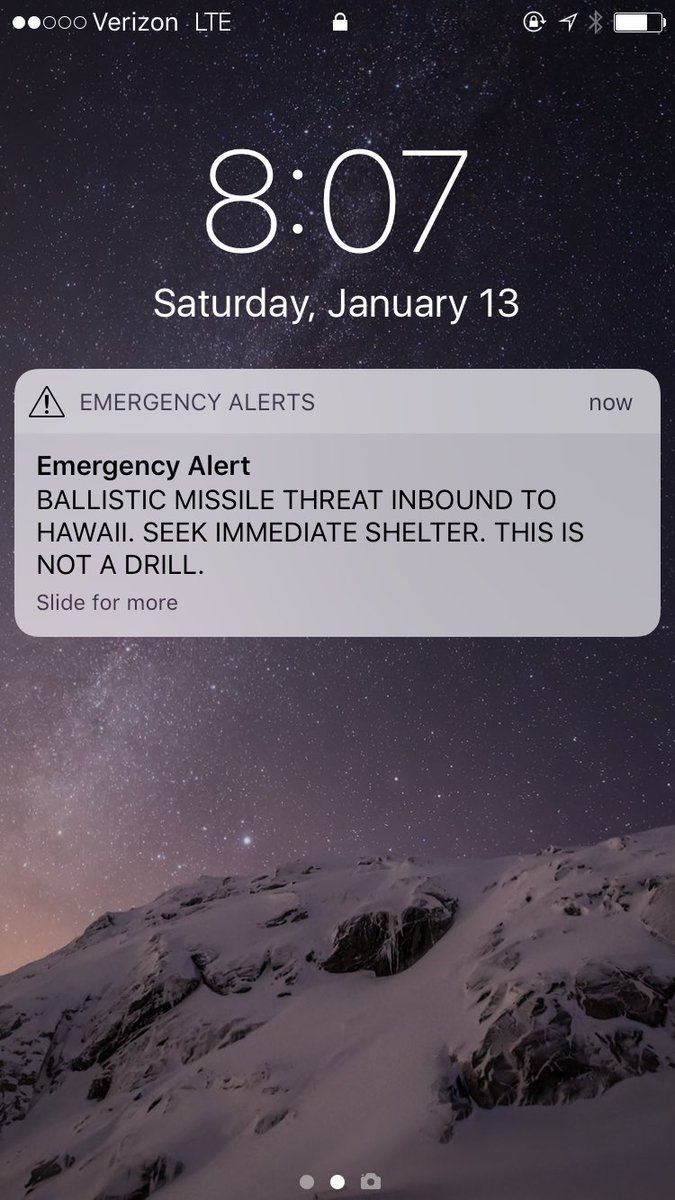
There is a small issue with the message. Guess what it might be. Go on, guess.
The Hawaii Emergency Management Agency just sent out a helpful text message:

There is a small issue with the message. Guess what it might be. Go on, guess.
This piece of art depicts the McDonnell-Douglas “Drawbridge” orbiter in orbit delivering a satellite. Note that the wing are deployed, even though they would be folded up during entry. The geometry of the craft was such that in order to get the cargo bay door open and payloads safely in and out, the wing needed to fold down out of the way.
This points out one of the reasons why you don’t often see a whole lot of “cool” stuff in aerospace… everything has tradeoffs. And needing the wings to constantly go up and down is a bit of a headache. When it comes to spacecraft, mass is a primary priority; the mechanisms needed to deploy the wings weight a lot… never mind the mechanisms needed to retract the wing again. As an example, the real space shuttle orbiter had no landing gear retraction system. And why should it? The landing gear is hardly something the Orbiter would ever need to retract. That could be done by the ground crew without adding weight and complexity to the craft itself.
Note that the Orbiter and the payload here seem to have not NASA markings, but Red Cross markings. I suspect that a number of variants of this piece of art would have been produced with several different markings (NASA and Pan Am being the obvious ones), but why exactly Red Cross? Dunno.
Also note that this might not be an actual “Drawbridge” design, as no extension mechanism for the wing s in evidence. This might be an oversight on the part of the artist; it might be that this was a fixed-wing design. Given the RCS thrusters on the wingtips, this is most likely *not* a Drawbridge.
I’ve uploaded the high-rez version of this artwork (11.2 megabyte 6271×4763 pixel JPG) to the APR Extras Dropbox folder for 2018-01, available to all APR Patrons at the $4 level and above. If you are interested in accessing this and other aerospace historical goodies, consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
While poking around one of my old computers I found the partially finished 3D CAD model of the Martin “Aldebaran” I made some years ago for my NPP book. I’ll use the model to create diagrams for the book, in hopes that someday I’ll finish the damn thing, but I’m curious if there might be interest in physical models of the thing. Let me know. I might take a stab at this with Shapeways or some such.
The rewards for APR Patrons have been issued. This month:
CAD Diagram: Marquardt hypersonic burning ramjet booster
Diagram: Convair Class VP Airplane High Performance Flying Boat
Document 1: Apollo Exploration Shelter System
Document 2: Chrysler Work Station Capsule (“work pod” for astronauts)
Document 3: Sikorsky S-97 “Raider” brochure
If you are interested in helping to preserve (and get copies of) this sort of thing, consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
This piece of art depicts the McDonnell-Douglas “Drawbridge” orbiter staging off the manned flyback booster, showing the wings still folded against the sides of the fuselage. The wings served no purpose during ascent; they would only be used after-re-entry. Of course, in the event of a mission abort shortly after launch, the wings would need to deploy fairly quickly. There are no doubt numerous abort scenarios where the orbiter would be left intact after separation from a presumably stricken booster (or after a main engine failure on the orbiter stage), but would nevertheless still be doomed due to inability to get the wings deployed in time.
I’ve uploaded the high-rez version of this artwork (5 megabyte 3951×2121 pixel JPG) to the APR Extras Dropbox folder for 2017-12, available to all APR Patrons at the $4 level and above. If you are interested in accessing this and other aerospace historical goodies, consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
Another project under development…
For about three weeks the world has been uncertain whether Elon Musk was serious or not with his claim that the first launch of the SpaceX Falcon 9 Heavy would send a Tesla Roadser to Mars (well, onto a solar orbit that would zip past Mars). Turns out he wasn’t kidding:
This… makes sense. It is standard for a new launch vehicle to not launch a paying payload, because the first launch of a new vehicle stands a fair chance of not working right. So they launch inert mass simulators. So… why not launch a car? It’s attention-getting, it builds on corporate branding, it’s newsworthy. But mostly…
Sure, it would be better to send a practical payload… space probes and the like. But the fact is that there isn’t a Space probes R Us superstore; these things are extremely rare and extremely expensive. You lose one of those things, and there’ll be a whole lot of financial trouble. But Tesla Roadsters? Bunch of ’em.
The early development of the Space Shuttle was filled with bizarre designs, attempts to jam capabilities into existing technologies. One such unconventional concept came from McDonnell-Douglas: a low-cross-range orbiter atop a flyback booster. The orbiter, unlike the Shuttle Orbiter actually built, contained considerable internal propellant; the booster would get it up to high altitude and velocity, but the bulk of the actual delta V would come from the Orbiters own propulsion. The vehicle had small, straight wings that would fold up against the side of the fuselage for launch and for re-entry… but they would have to deploy on-orbit to allow the payload bay doors to open, and they’d deploy again once the craft had entered the atmosphere.
I’ve uploaded the high-rez version of this artwork (8 megabyte 5598×4529 pixel JPG) to the APR Extras Dropbox folder for 2017-12, available to all APR Patrons at the $4 level and above. If you are interested in accessing this and other aerospace historical goodies, consider signing up for the APR Patreon.
A few days ago I uploaded in the 2017-12 APR Patron Extras Dropbox folder a scan of an old magazine article on the X-24 lifting body which including this interesting piece of art depicting an X-24 atop a Titan IIIc launch vehicle. There were indeed proposals to launch X-24 derivatives into orbit with Titan IIIs, but they wouldn’t be *exactly* X-24’s. The X-24 was not built as a spacecraft or a re-entry vehicle; it would be uncontrollable outside the atmosphere and would be a molten collection of rubbish on re-entry. Still, the proposed vehicles did look a *lot* like the X-24.
Support the APR Patreon to help bring more of this sort of thing to light!
There is apparently some discussion about parking some THAAD missiles along the west coast to protect against the likes of a Nork missile. The THAAD isn’t a full-up anti-ICBM system, but it’s the best the US currently has for land-based systems. It’s also the only missile in operation that has an important subsystem (the igniter) designed by *me.* So there.
There is, of course, no actual money for this.