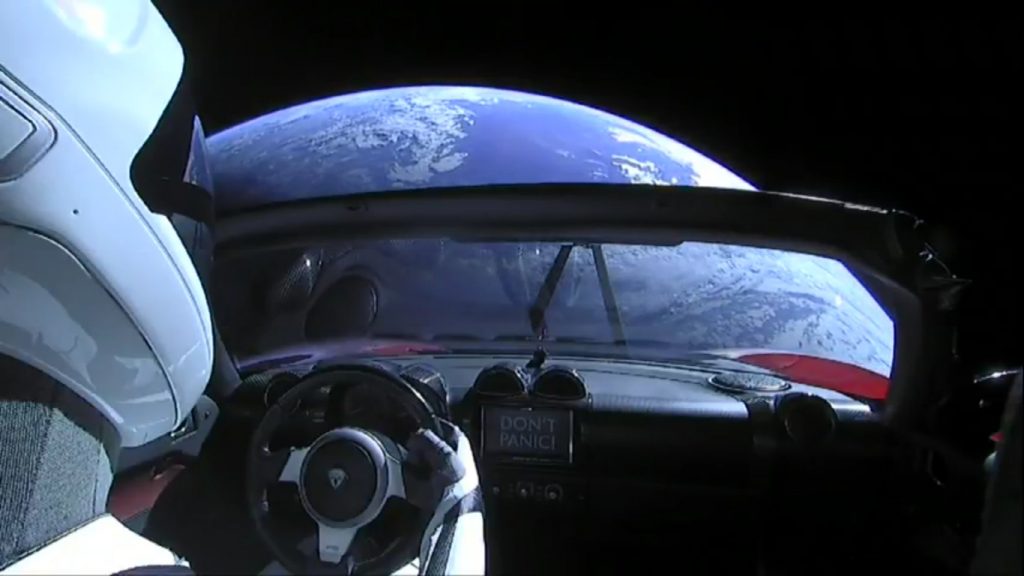
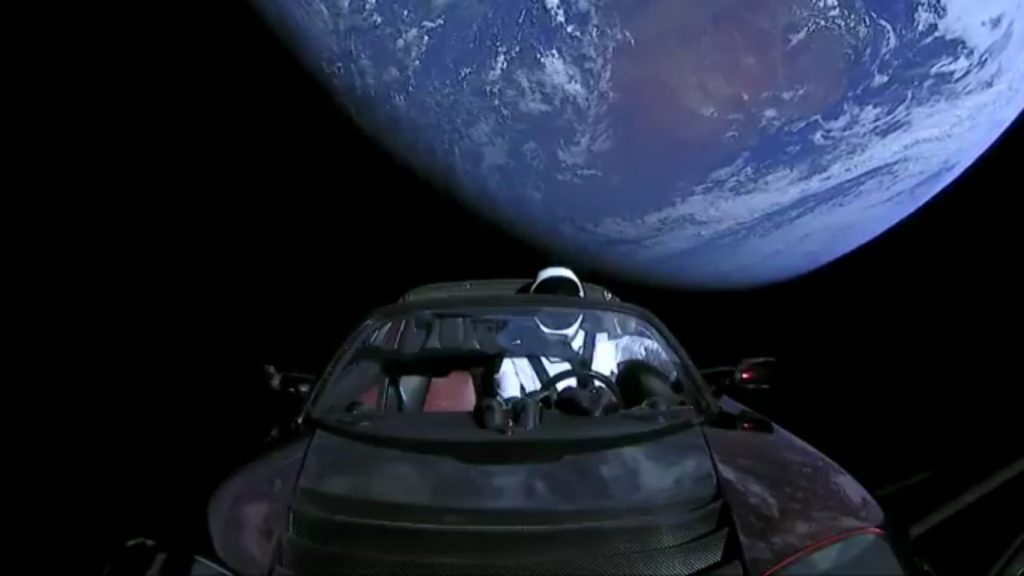
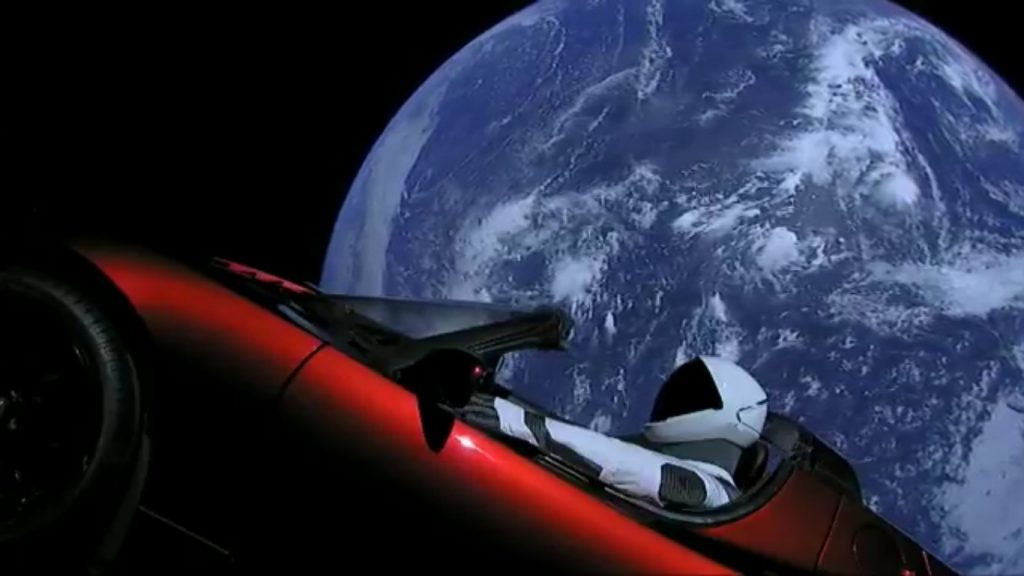
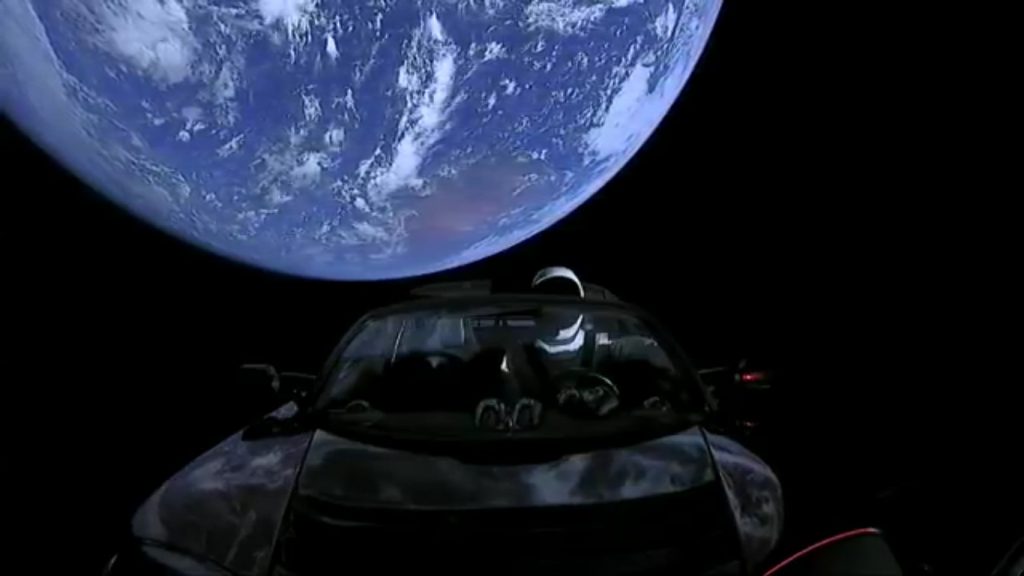
The Falcon 9 Heavy flight went off seemingly without a hitch (as I write this it’s not yet clear if the core booster landed right on the barge EDIT: Whoopsie, the core smacked into the water near the barge at a stately 300 miles per hour due to a failure to ignite two of the three braking rockets). But the two boosters landing simultaneously, side by side… that is hands down no BS the coolest, awesomest, most hopeful thing I’ve ever seen. I’m beyond jealous of the people who work at SpaceX.
How awesome is this? It’s all the awesome. Give it up, Star Wars. There’s no awesome left for you.

Now would be the time for trump to get on live TV and say, in effect, “USA! USA! USA! This is what free men in a free market can do. It’s hyuuuge. It’s beyootiful. And I’m’a gonna take all the moneys the US current sends overseas and instead will pay SpaceX to launch a Trump Casino And Resort to Velles Marinaris.”