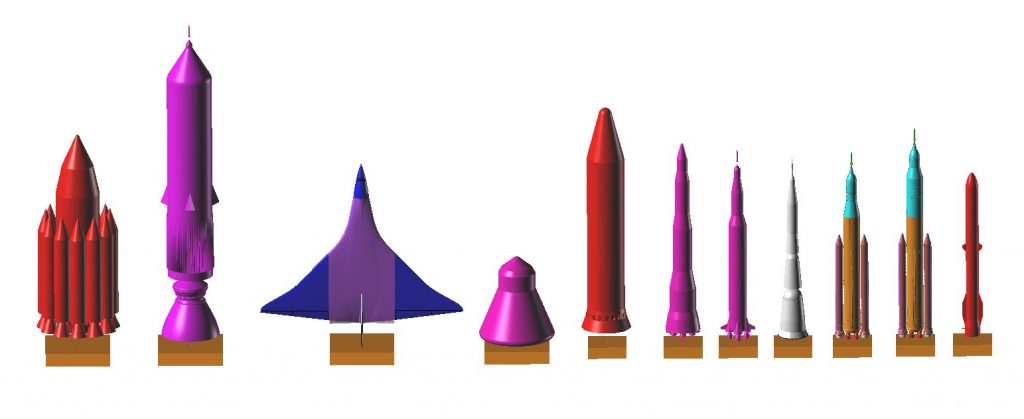
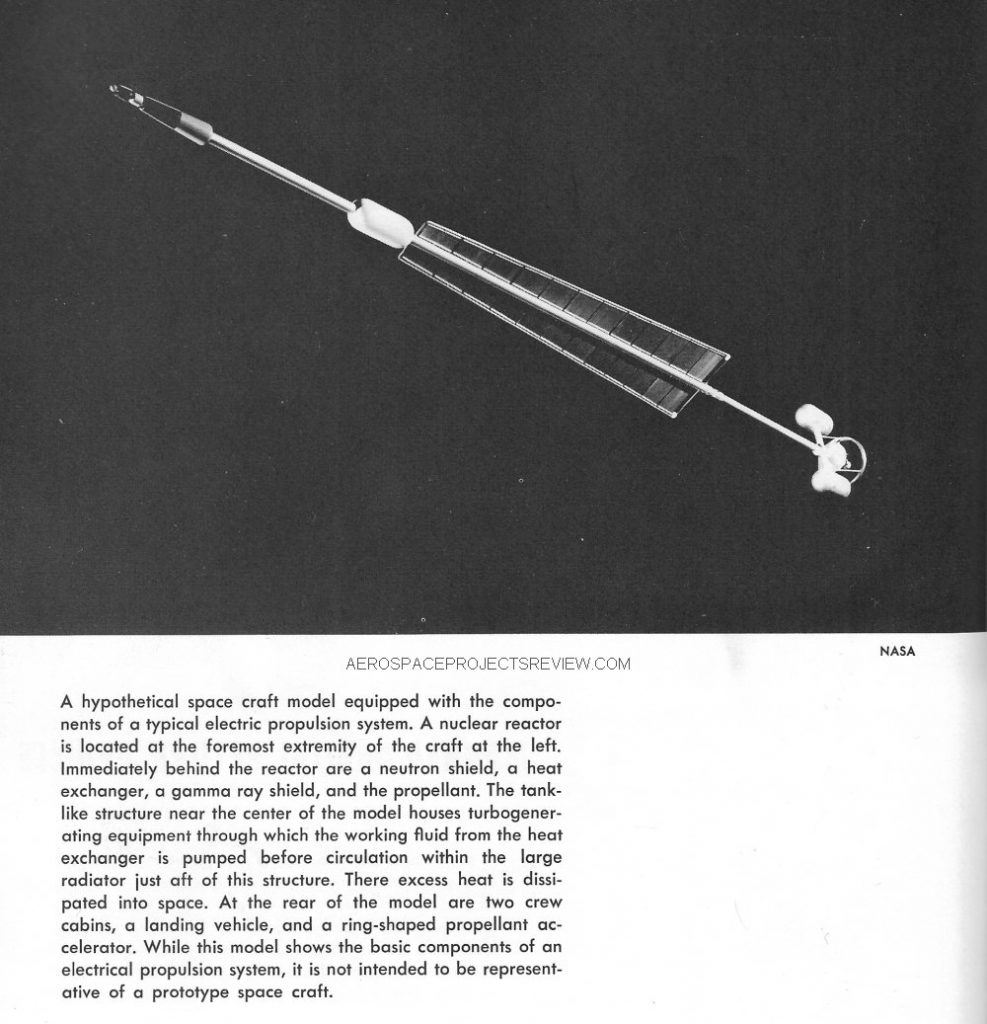
As previously mentioned, I’m tapping away at a CAD model of the Star Raker for the primary purpose of diagrams & art for the next issue of US Launch Vehicle Projects, and the secondary goal of a model kit. The plan at this time is to produce the Star Raker as a 1/288 scale model. That’s a slightly unusual scale; most launch vehicle models are in 1/144 or even 1/72 scale. But the Star Raker… she was huge. It was a horizontal takeoff airbreathing single stage spaceplane designed not to resupply a space station or any such trivial task, but to deliver to low Earth orbit the raw materials with which to build solar power satellites. it’s payload would have been small by the reckoning of most SPS launchers, which tended to have megapound-class payload capacities, but it still would have rivaled the Saturn V. To do that with a winged vehicle meant that its wings were vast, spanning 375 feet.
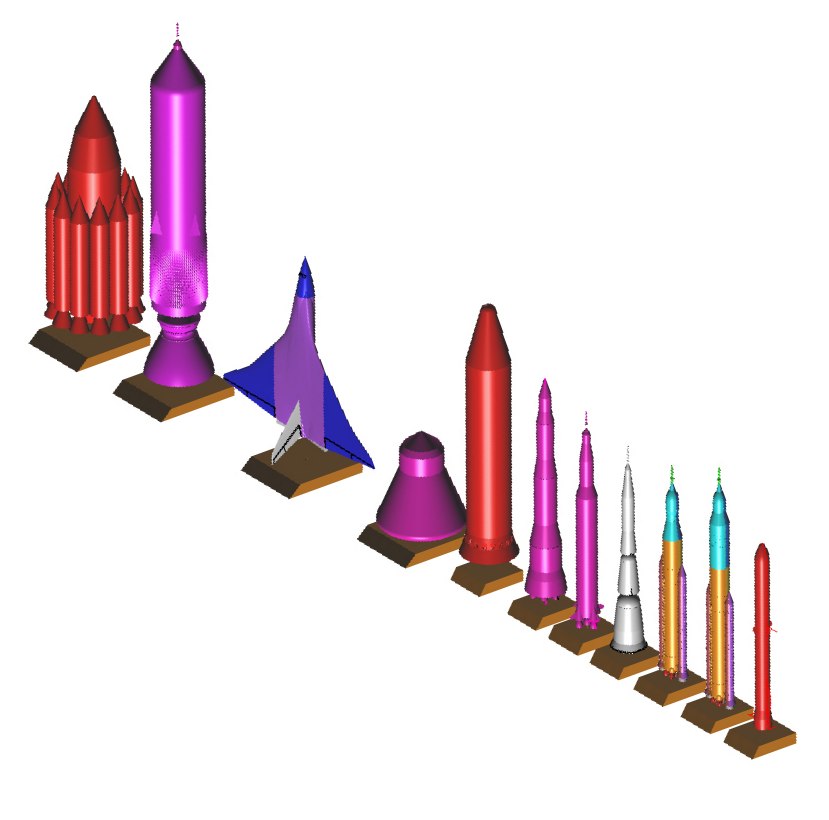
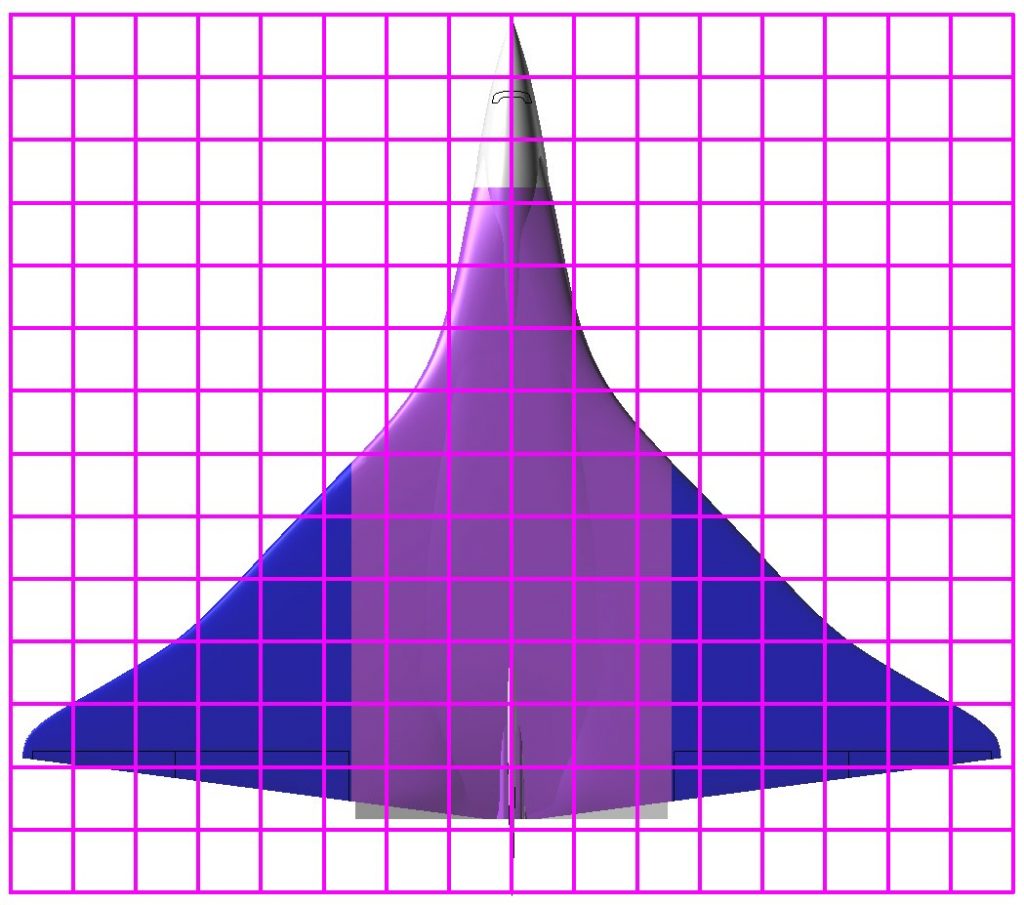
Here is a basic render of the model as it currently stand. the overlaid grid shows how big the 1/288 kit will be: each grid is one inch. You would not feel ashamed to have this sit on your desk or bookshelf.
My goal with this model is to have a relative *few* bits of extra details. Cockpit and landing gear would be tiny and pretty much infeasible at this scale, and there were no underslung weapons or gun turret or any such thing. Consequently the part count should be low. The model is being designed for the best simplicity possible in order to keep the price as low as feasible. A model kit is as yet not a sure thing. So if you know anyone who might be interested, let them know.
Something I think might look good, once the USLP project is done, is to continue with the diagramming and go into some detail and produce a large-format print of some kind, either cyanotype or mylar…