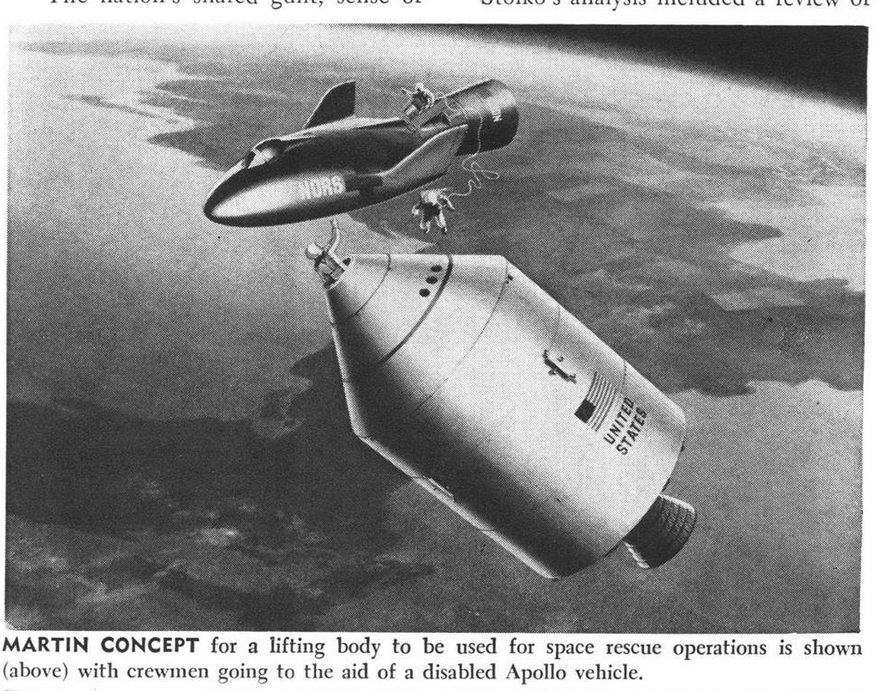
The 1969 movie “Marooned” featured an Apollo crew stranded in orbit and eventually rescued by a lifting body spacecraft,the fictional “XRV.” It has been noted that the vehicle and the basic setup look a *lot* like an illustration from a 1965 issue of Aviation Week depicting a Martin Co. lifting body rescuing the crew of an Apollo spacecraft:
There is clearly something a little strange going on in this artwork: what may seem like an adapter section or a propulsion module behind the lifting body is actually a docked Gemini spacecraft. There is no explanation for this, but I can speculate. The lifting body is meant to serve as a rescue craft, so it would need to have as much internal space as possible. Not just for three rescued Apollo astronauts, but three astronauts potentially in medical distress. So they might need to be laid out on stretchers, not just sitting in seats. Consequently, while they would need a pilot to get them home and “ambulance staff” to get them squared away, there might not be enough room for everyone. So *perhaps* what’s going on here is that the spaceplane is launched empty or with just a pilot, and the Gemini/Adapter has two EMTs in it. They get the rescuees dealt with and sent home, and they come home in the Gemini. This way, three rescuers go up, but only one comes down taking up space in the lifting body. This is non-optimal, of course; better would be to bring everyone home in one large vehicle. But perhaps this was the best that could be done with the intended launch system, presumably a Titan IIIc.
The lifting body is clearly related to the X-23/X-24 geometry that Martin was beginning to study at the time. A mockup that is very similar, though with the central vertical stabilizer that eventually appeared on the X-24, is shown HERE and HERE.