Now available… four new issues in the US Aerospace Projects line.
US Fighter Projects #3
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Fighter Projects #03 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #3 includes:
- Vought Advanced Interceptor AI-0604R: a dart-winged ejector ramjet-powered concept
- Convair Nuclear Powered Interceptor Configuration I: a single0seat interceptor with a nuclear reactor
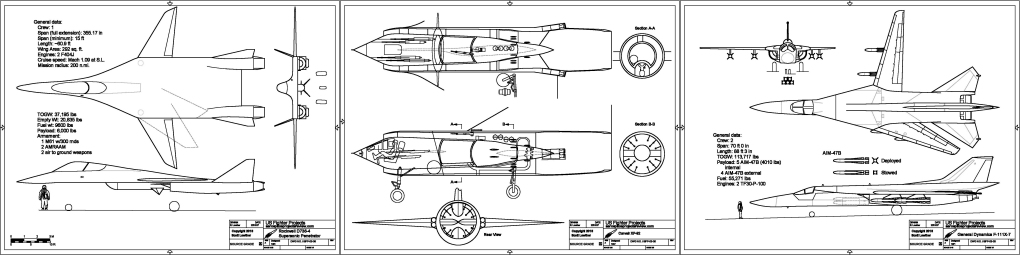
- General Dynamics F-111X-7: A stretched F-111 for bomber escort and interception
- Bell Ramjet Fighter: A subsonic small fighter from the end of WWII
- Convair XP-92: A post-war delta-winged ramjet powered supersonic interceptor
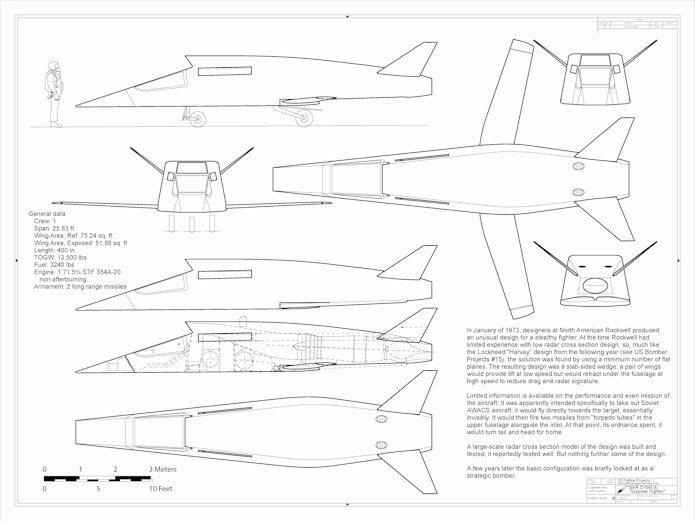
- Rockwell D736-4 Supersonic Penetrator: the wings could sweep back entirely within the fuselage
- Lockheed CL-362-2: A high-altitude hypersonic rocketplane
- NASA-Langley TBF-1: an unusual supercruiser
USFP #3 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4.25:
——–
US Launch Vehicle Projects #5
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Launch Vehicle Projects #5 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #5 includes:
- North American Aviation 600K SSTO: an early concept for cheap space launch
- Boeing “Windjammer” SSTO: A horizontal takeoff design form the early 70s
- JSC Winged Heavy Lift Launch Vehicle: A giant SPS launcher
- NASA Nova “Saturn C-8”: an early Apollo booster
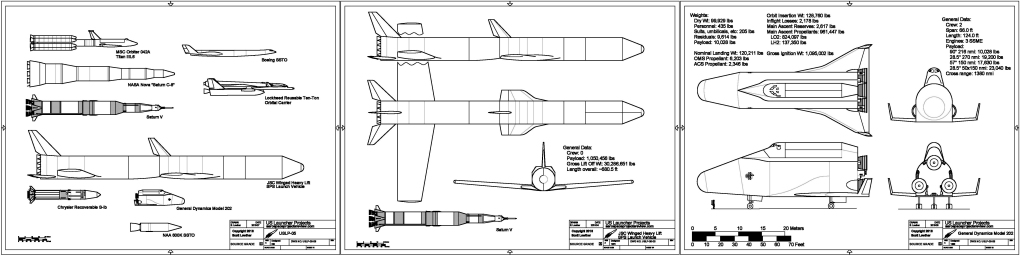
- Lockheed Reusable Ten-Ton Orbital Carrier: A logistics system from the early 60s
- Chrysler Hot Air Balloon S-IB: An unusual approach to booster recovery
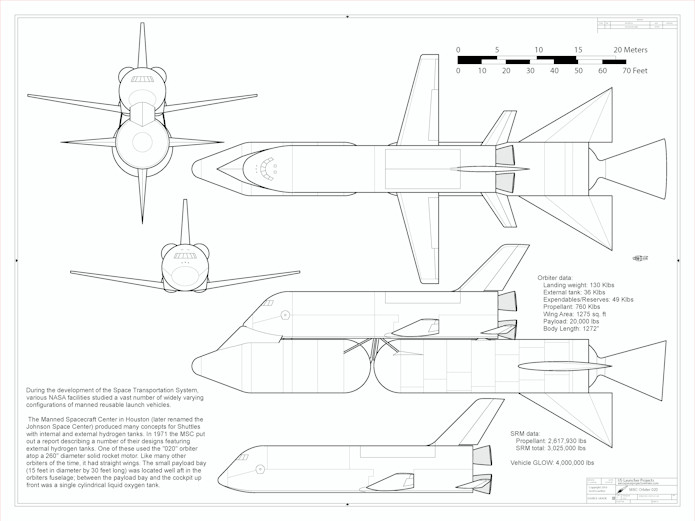
- MSC Orbiter 042A Titan IIIL6: A shuttle design with a delta-winged orbiter on an enlarged Titan
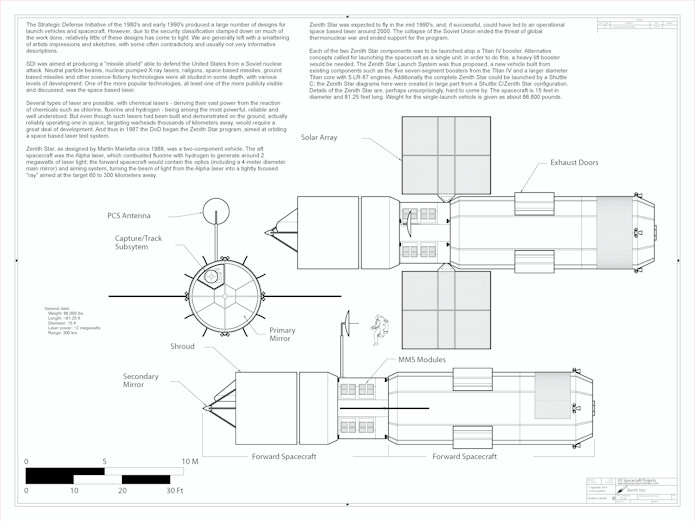
- General Dynamics Model 202: a preliminary design for a Brilliant Pebbles launcher
USLP #5 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4.25:
——–
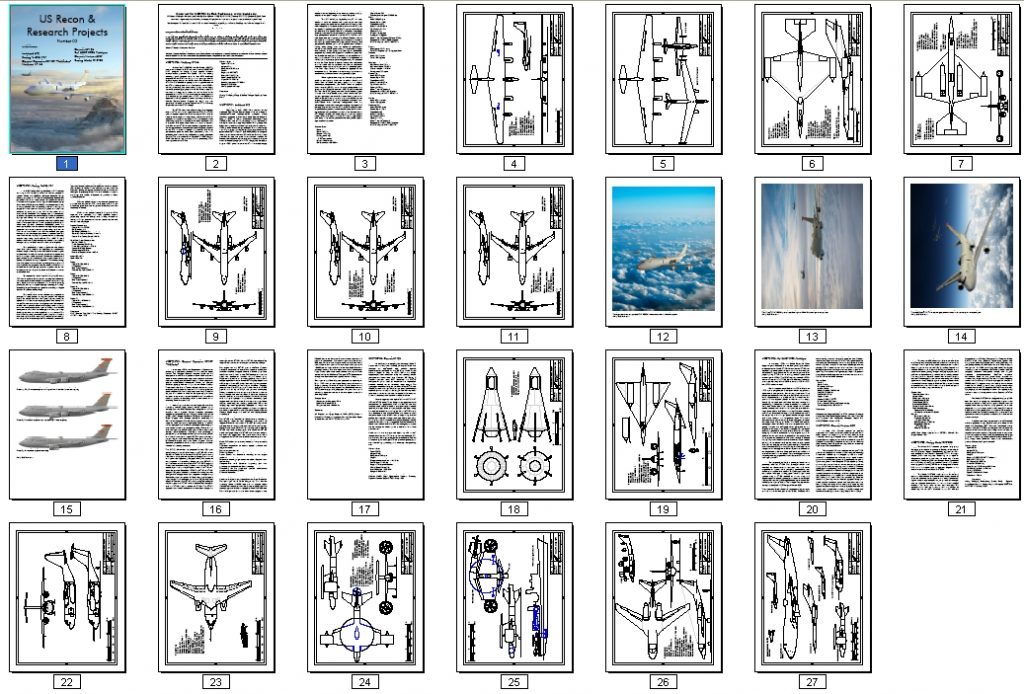
US Recon & Research Projects #3
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Recon & Research Projects #3 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #3 includes:
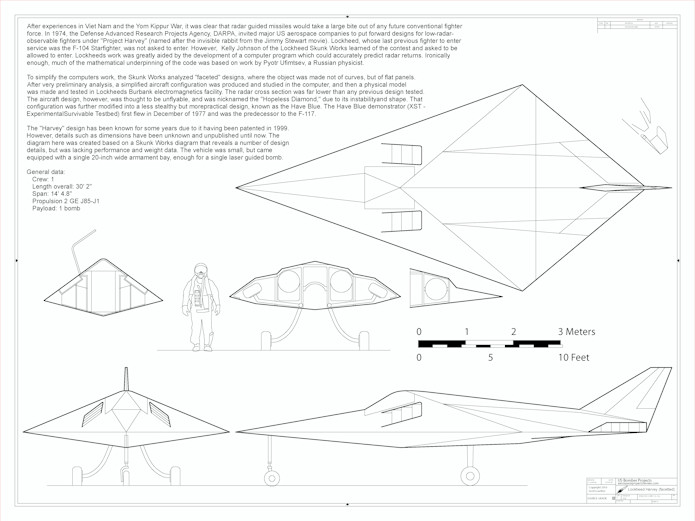
- Lockheed A-2: An early design leading to the SR-71
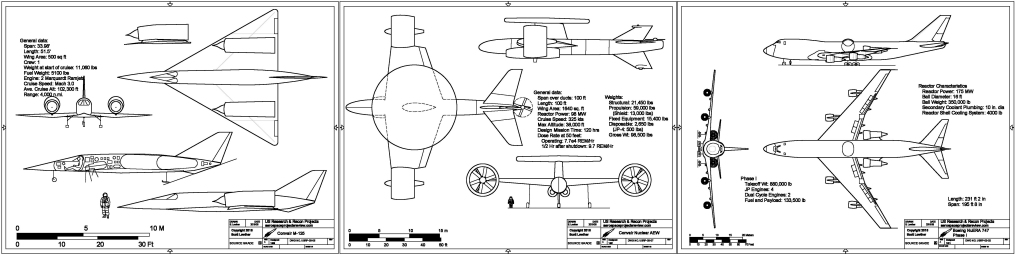
- Boeing NuERA 747: A nuclear powered 747
- General Dynamics SX-109 “Pathfinder”: a subscale SSTO demonstrator
- Northrop N-165: A giant U-2 alternate
- Convair M-125: A high altitude/speed single seat recon plane with toxic fuel
- Bell AMST STOL Prototype: A heavily modified C-130
- Convair Nuclear AEW: unmanned, nuclear powered VTOL fleet defense recon platform
- Boeing Model 818-300: an early 60s battlefield surveillance platform
USRP #3 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4.25:
——–
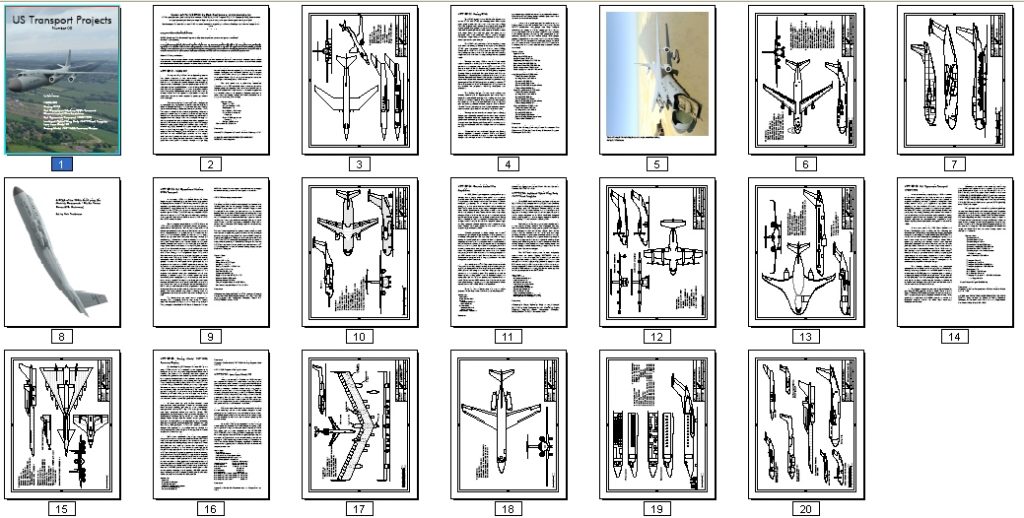
US Transport Projects #8
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Transport Projects #8 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #8 includes:
- NACA SST: a 1947 concept
- Boeing CX-HLS: Boeings design for what became the C-5
- Bell Operational Medium STOL Transport: vectored thrust for short takeoff
- Convair Limited War Amphibian: A concept for a single plan to meet both land and sea plane requirements
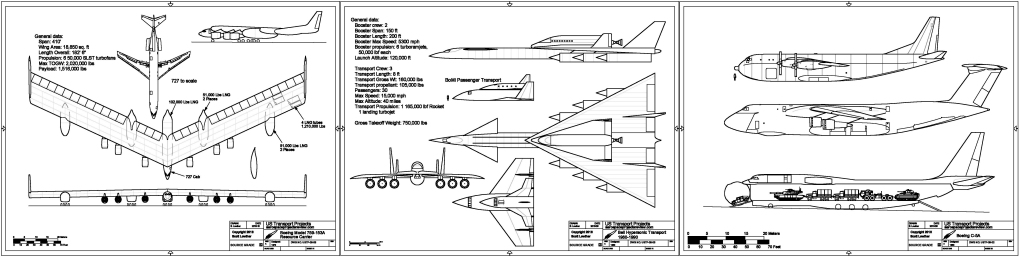
- Bell Hypersonic Transport 1980-1990:A two-stage turboramjet/rocket concept
- Lockheed Hybrid Wing Body 757PF-Sized Freighter: a recent design for an advanced transport
- Lear Liner Model 40:a small airliner/large executive transport
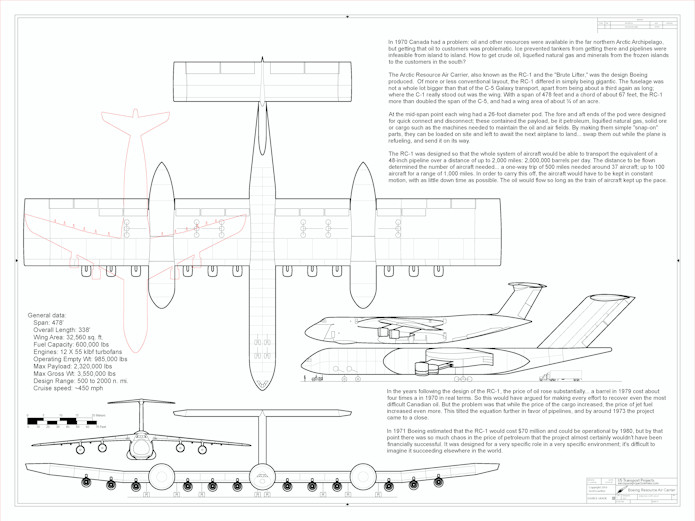
- Boeing Model 759-153A Resource Carrier: A big flying wing natural gas “tanker”
USTP #8 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4.25:
——–