Now available… the newest and biggest issue in the US Aerospace Projects line.
US Launch Vehicle Projects #6
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Launch Vehicle Projects #06 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #6 is devoted to the launch vehicles proposed for the 1970’s Solar Power Satellite program. This required millions of tons of payload delivered into Earth orbit over a span of decades, with flight rates of several times per day for each vehicle. This program produced some of the largest and most ambitious launch vehicles ever designed, and was the last time that launchers of this size were ever seriously contemplated. Appropriately, USLP#6 is by far the largest issue of US Aerospace projects to date at over seventy pages, three times the size of a usual issue.
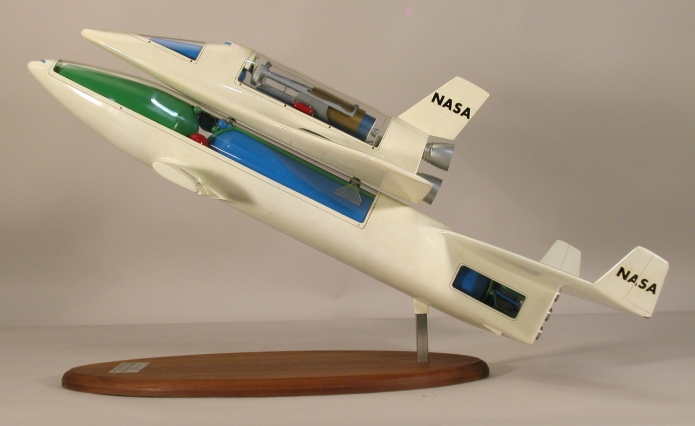
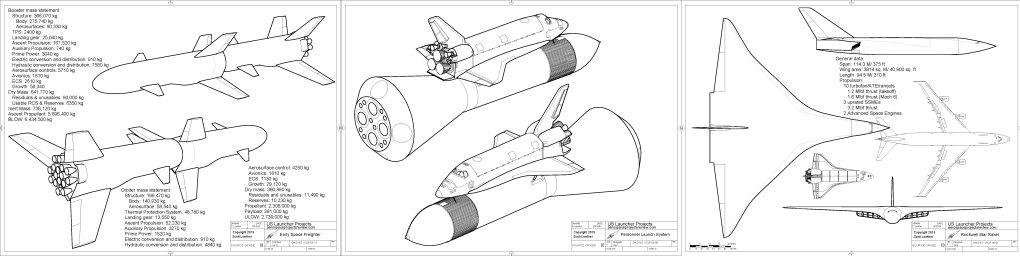
Topics in this issue include the Rockwell Star-Raker, several Boeing Space Freighters, the Boeing “Big Onion” Low Cost Heavy Lift Vehicle (antecedent and descendant designs), a Grumman two-stage HLLV, a Rockwell HLLV and “small” HLLV, NASA-JSC heavy lifters, a Boeing/Rockwell Personnel Launch Vehicle and a Boeing winged SSTO. Along with orthogonal views, a number of perspective diagrams are also included.
USLP #6 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $9:
——–