One sizable document I’ve scanned for preservation is a Rockwell presentation package from October, 1985, showing a large number of space programs that the company could capitalize on. These included everything from minor mods to the Space Shuttle to major changes… stretching the orbiter, stretching the tank, adding additional boosters. Heavy lift boosters to put SLS to shame; heavy lift SSTOs; small experimental spaceplanes; manned military spaceplanes; space-based weaponry; space stations; space based nuclear power. Figured this stuff might be of some modest interest. So why not, I’ll post little bits of it from time to time.
Rocket Lab is, it seems, planning on recovering and reusing the first stage of their small Electron launch vehicle. The means of recovery is a lot lower tech than that of the Falcon 9… the Electron will pop a drogue ballute to stabilize, then open a parafoil to slow down and drift in the direction of a recovery ship. Before splashdown it will be air-snatched by a large helicopter then flown to the ship. Should be doable; the small size of the booster makes recovery of the entire first stage via this method practical, while Lockheeds Vulcan is, last I checked, only planning on recovering the engines and avionics.
This is of course no threat to SpaceX, which is going increasingly Bigger And Bigger. Still, it will be good to see yet more space launch systems working towards reusability and truly low cost.
On the other hand: no matter how capable Rocket lab gets with future boosters, their choice of launching from new Zealand will be a limiting factor. New Zealand has been since 1984 a “nuclear free zone,” excluding from its territorial waters any ship powered by nuclear reactors. While this would not necessarily seem to exclude nuclear powered spacecraft… why would someone with such a payload risk it?
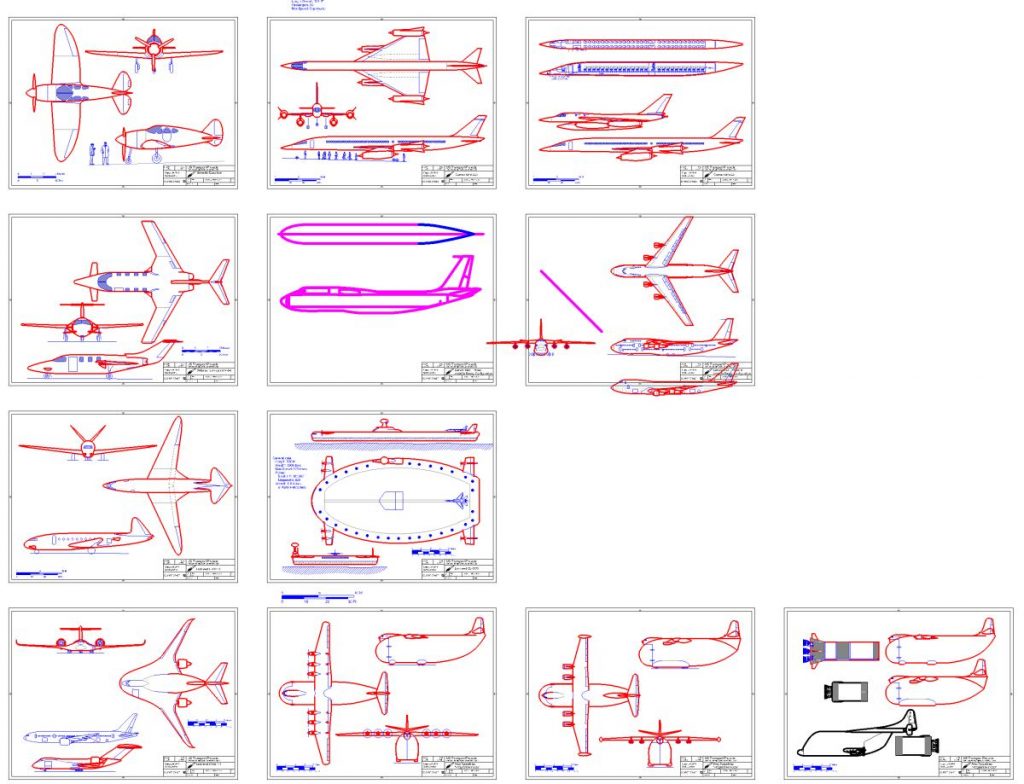
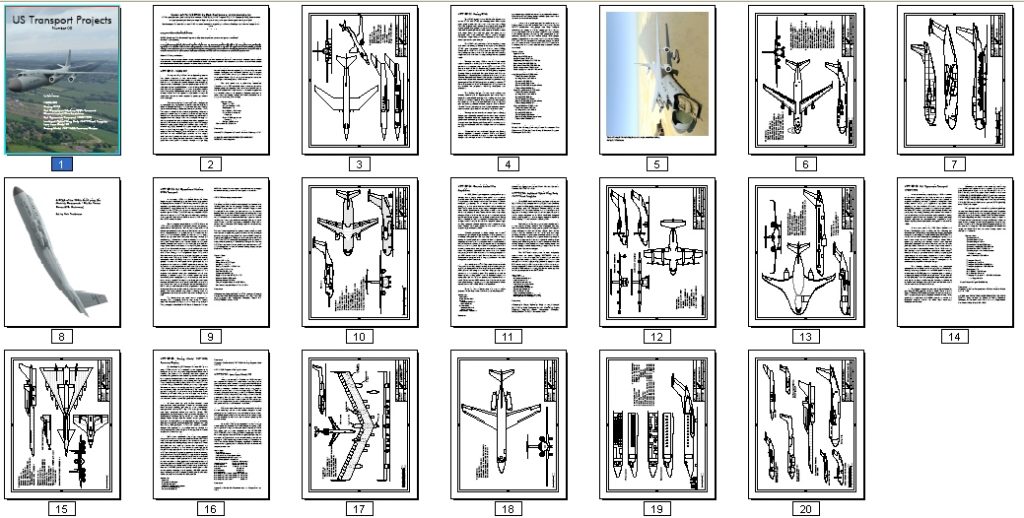
Just finished the initial cut of diagrams for US Transport Projects #9, except for the interior layout of one jetliner…
Previously…
US Transport Projects #8
Cover art was provided by Rob Parthoens, www.baroba.be
US Transport Projects #8 is now available (see HERE for the entire series). Issue #8 includes:
- NACA SST: a 1947 concept
- Boeing CX-HLS: Boeings design for what became the C-5
- Bell Operational Medium STOL Transport: vectored thrust for short takeoff
- Convair Limited War Amphibian: A concept for a single plan to meet both land and sea plane requirements
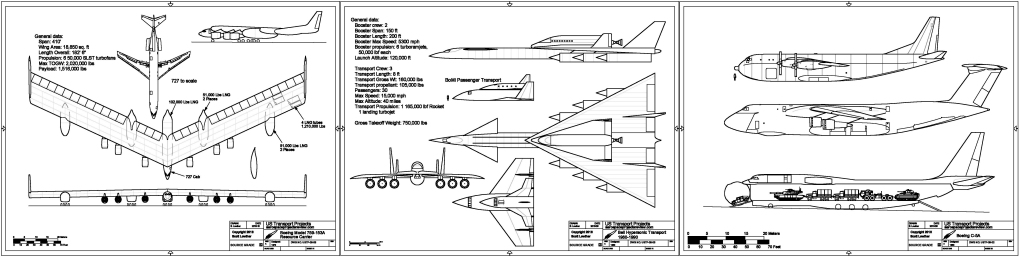
- Bell Hypersonic Transport 1980-1990:A two-stage turboramjet/rocket concept
- Lockheed Hybrid Wing Body 757PF-Sized Freighter: a recent design for an advanced transport
- Lear Liner Model 40:a small airliner/large executive transport
- Boeing Model 759-153A Resource Carrier: A big flying wing natural gas “tanker”
USTP #8 can be downloaded as a PDF file for only $4.25:
——–
Hmmmm…..
SpaceX CEO Elon Musk says first orbital Starship prototype flight debut is just weeks away
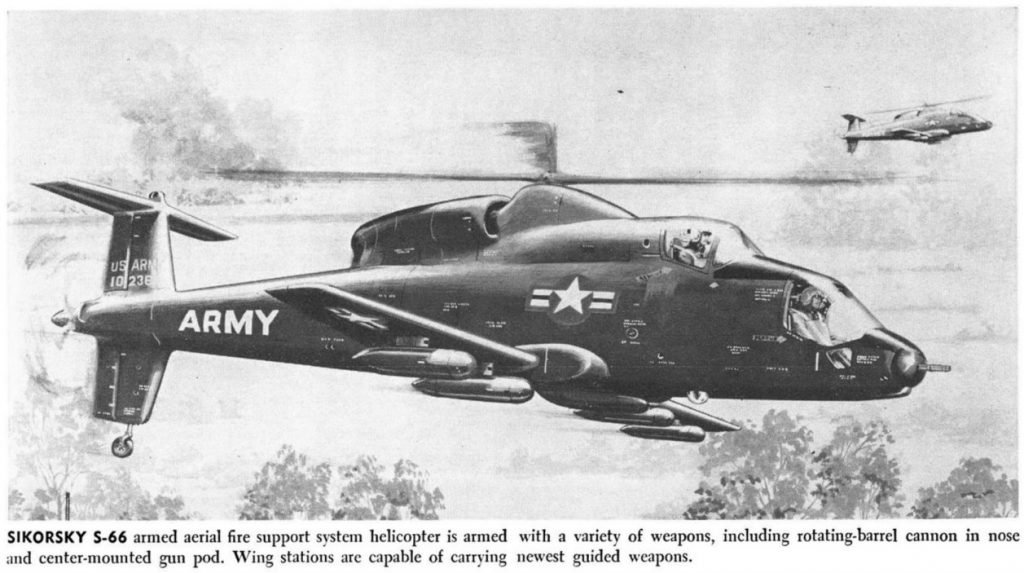
In 1964 Lockheed put forward a design in the US Army’s Advanced Aerial Fire Support System (AAFSS) program that would eventually win and become the AH-56 Cheyenne. But Lockheed was not alone in tendering a proposal: Sikorsky entered their S-66 design.
Both helicopters would have been advanced and fast. Lockheed made the AH-56 fast by adding a pusher prop to the tail, just aft of the conventional anti-torque rotor. But Sikorsky went a slightly different route: the S-66 used the “rotaprop” tail. This combined anti-torque duties with forward thrust in a single mechanism… a single somewhat complicated mechanism that could turn the sideways-thrusting anti-torque rotor 90 degrees to point it aft, providing forward thrust. This would have decreased drag and potentially decreased weight, but at added technical risk compared to the relatively simple solution of just adding a dedicated pusher prop. In late 1965, the Army decided that the risk was too high, and went with Lockheeds design.
The S-66 design got a fair amount of publicity during the contest, but I’ve never actually run across the proposal documentation or design diagrams. A few photos of a display model and a single cutaway drawing are presented HERE. Below are some magazine illustrations of the S-66. It would have been an impressive helicopter had it been built and if it had been successful, looking not unlike a sleeker version of the Mil 24 Hind attack helicopter.
It seems that Boeing, prime contractor for the Space Launch System, tried to shut down development of orbital fuel depots and orbital propellant transfer. Because if you can stash a lot of fuel in orbit easily and cheaply, you don’t *need* the bloated irrational monstrosity that is SLS.
The SLS rocket may have curbed development of on-orbit refueling for a decade
What’s interesting; if this story is true, Boeing opposed fuel depots because they threaten SLS. But SpaceX, now working on “Super Heavy” rockets with roughly the same capability as SLS, are *actively* supporting fuel deports. Why the difference? Because SLS was never meant to really do anything. Launch once a year, one extremely expensive mission maybe to the moon, call it good. Pretend to be moving outwards again, but the minimum possible steps taken as slowly as possible. SpaceX wants to lob dozens of people to *Mars* in just the next few years. Same launch capability, but fundamentally different goals.
*IF* this story turns out to be true, someone needs to have their ass handed to ’em. Congressional investigations at least on par with the “Trump is a Russian stooge” investigation, because this one has had clear and obvious impacts on the US: Billions spent on a system nobody wants, years wasted that that the US could have used to conquer the heavens. Hell, just imagine what we could have done with SLS money by way of building breeder reactors.
Before Lunar Orbit rendezvous made it possible for a single Saturn V to launch a complete lunar mission, the expected mission profile included launching a rather large lunar lander to Earth orbit, mating it with n upper stage, and then fueling the whole thing using specialized tanker spacecraft. NASA lucked out with the LOR concept; while some considerable work had been done on the tankers, the fact is that NASA really didn’t know *how* to do zero-gravity propellant transfer. When the word came down to stop working on the tankers, there were undoubtedly quite a number of quiet expressions of relief.
Still: the ability to do major propellant tanking in space will be vital for a real interplanetary economy. SpaceX will need to be able to do that for many of the lunar and Mars missions planned for Starship. So, it seems that on-orbit tanking is back on the menu.
NASA agrees to work with SpaceX on orbital refueling technology
Not much to see in this video, since it occurred at night and was shrouded by smoke and vapor. Presumably better video will emerge. But the StarHopper seems to have done what it set out to do… it went up, it translated, it came down and it didn’t kerplat or kerplode.
A quarter century ago I went out of my mind watching the Delta Clipper do this. Now, it’s more “Huh. Well, that’s good.” Because one gets used to seeing amazing things, I suppose, which explains why people stopped caring about Apollo and didn’t string up LBJ when Apollo was strangled in the crib. Fortunately for SpaceX, they don’t need to keep the masses entertained… they just need to keep Elon Musk entertained. And hopefully he won’t be done being entertained until there is a self-sustaining space infrastructure in place.
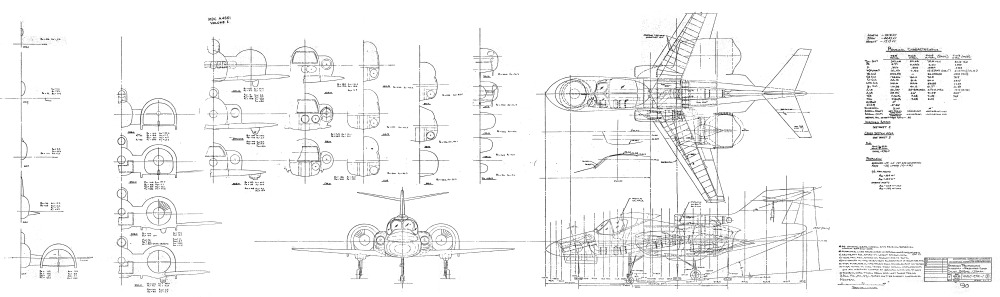
McDonnell Douglas spent much of the 1970’s trying to get NASA, the Marines and the Navy to fund the development of a lift-fan-based VTOL aircraft concept, the Model 260. This general concept showed up in a number of different forms, from strike bomber to carrier onboard delivery transport to Marine troop transport. Shown below is a”Research Technology Aircraft,” a proof of concept prototype to be assembled from existing aircraft components, much as Rockwell did with the XFV-12.
I’ve made the full resolution version of the diagram (equivalent to 37 inches wide at 300dpi) available to above-$10-subscribers of the APR Monthly Historical Documents Program/Patreon.
If this sort of thing is of interest, consider subscribing. Even a buck a month will help out; but the more you subscribe for, the more you get… and the more you help me get from eBay and save for the ages.
A while back I sold a few copies of a prototype of a “Booklet of General Plans” for the Space Station V from “2001.” The feedback I got suggested that the idea has merits, and with some refinement it might be something interesting.
Along with Space Station V, I have made mention of wanting to do the same sort of thing with Clavius Base and The Orville. Clavius Base is a concept at a fabulously early stage. The Orville’s 3D model is long completed, but recent news is that Eaglemoss will release a line of Orville ships starting in 2020. Since the Eaglemoss Star Trek ships come with a small magazine that provides canonical in-universe data, I will wait to see what comes out at that time.
I have a number of other Booklets in various stages of completion. Some are still in the modeling stags; some require a whole lot of tinkering with the diagrams, some are in the writeup stage. Each will have text to go along with them that will be an in-universe description of the vehicle; the “Bird One,” for example, depicts a US government attempt to reverse engineer the design as best they can based on fragmentary data. The Ajax will be another US Government attempt to describe Mongo tech after the events of “Flash Gordon.” And of course some of these, such as the Dyna Soar and the 10-meter Orion, will be non-fictional descriptions.
For those nerdy and old enough to remember the glory days of the “Booklets of General Plans” that were released for various Star trek ships, you’ll remember the pages and pages of deck plans. With a lot of these, “deck plans” won’t really be possible… for Dyna Soar, there really wasn’t a deck, and for the Helicarrier there were *way* too many decks. So each Booklet will be its own thing, with diagrams, inboard profiles, etc. that are appropriate. I’m thinking of pricing these something like $2 per page, more or less. The basic set will be 11X17 sheets, folded in half and put in a letter-sized envelope; but I’m also contemplating a limited run of each possibly on better paper, and either rolled or bound within a 12X18 binder.
If this sort of thing is of interest, take a look and let me know in the comments which one or more appeal. This is a sloooow, long-term project, more hobby than anything. So if you want one… let me know. And let your friends who might want one know. A few others arne’t included below, such as the “Men Into Space” ship and the Boeing IMIS Mars craft, which will be a *huge* set.