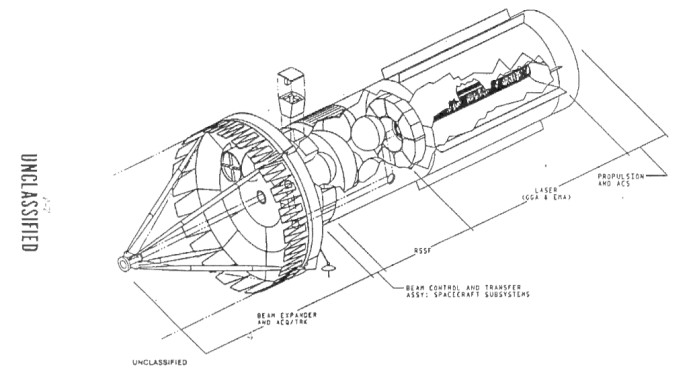
In 1985, Rockwell International contemplated the business case for Shuttle Derived Launch Vehicles. The specific design illustrated used the ET and SRB’s more or less stock, but the orbiter was replaced with a recoverable propulsion and avionics module. The payload came in the form of an upper stage with something very like the Apollo Command and Service Modules. This would probably have been for a lunar mission of some kind as a Shuttle-class booster is too big for a simple capsule mission to LEO. The basic design would have roughly performed like the presumably forthcoming SLS.
Point the first: it’ll be a bit lax on the blogging for the next little while. Got stuff to handle. Not, not coronavirus… not yet, anyway.
Point the second: color me stunned, Boeing done failed another aerospace project.
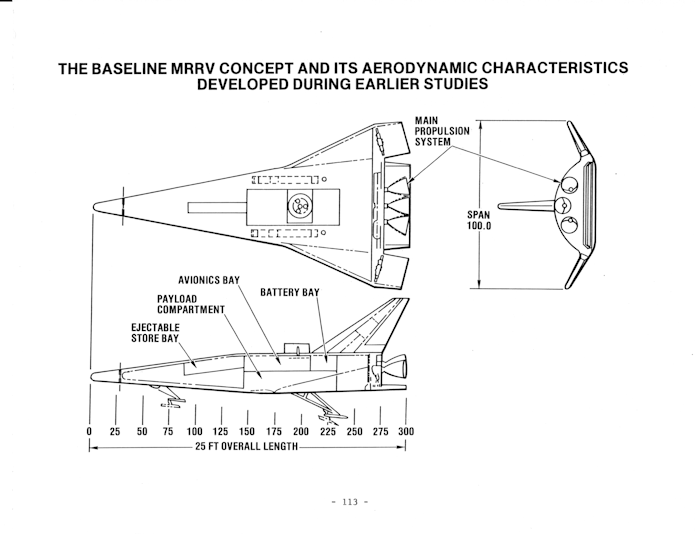
In 1985 Rockwell thought that there might be a business case for a small unmanned spaceplane for recon purposes. At the time, the answer was apparently no… but within a few years Rockwell developed the “REFLY” spaceplane which, over a span of a couple decades, transmorgified into the X-37B which has flown a handful of top secret long duration missions.
A piece of Lockheed concept art circa 1966 depicting a concept for a stowed-rotor helicopter, capable of efficient hovering performance as well as efficient high speed forward flight. This design is related to though distinct from the design depicted in artwork HERE. Note that the backgrounds of the two paintings share a lot of similarities… same ground structures, same leaves in the lower right. I don’t know if this means that one painting was copied from the other, or if one painting was painted *over* the other. In which case… as noted on the other post, I actually own that other piece of artwork. Buried under that upper layer of paint might be *this* image. Ain’t no way I’m going to scrape the paint off just to check, but the technology exists to X-Ray it to look for what’s buried underneath. Not that I’m going to do *that* either…
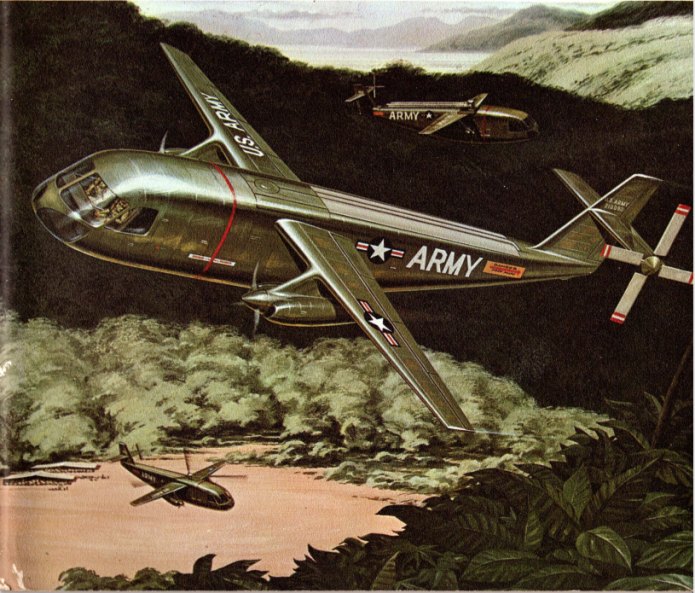
This aircraft is shown operating in Viet Nam, in US Army colors. This would have irritated the hell out of the US Air Force; by 1966, the USAF was to have control of all fixed wing combat aircraft. The role for this aircraft in Viet Nam would have been search and rescue rather than the transport of troops or ground attack, but still the USAF would have objected.
This piece of art came from a magazine article published in 1966. The full article has been scanned and saved as a PDF, made available to all $4 and up APR Patreons and Monthly Historical Document Program subscribers. it has been uploaded to the 2020-01 APR Extras folder on Dropbox for Patreons and subscribers. If interested in this piece or if you are interested in helping to fund the preservation of this sort of thing, please consider becoming a patron, either through the APR Patreon or the Monthly Historical Document Program.
In the 1980’s, military spaceplanes were all the rage… at least on paper. In 1985 Rockwell International considered the possibility that there would be a profitable business case for a relatively small manned spaceplane that could serve as a rapid-reaction launch system for missions such as recon. Thirty years later the X-37 finally accomplished something sorta along those lines, though without the crew and rapid reaction.
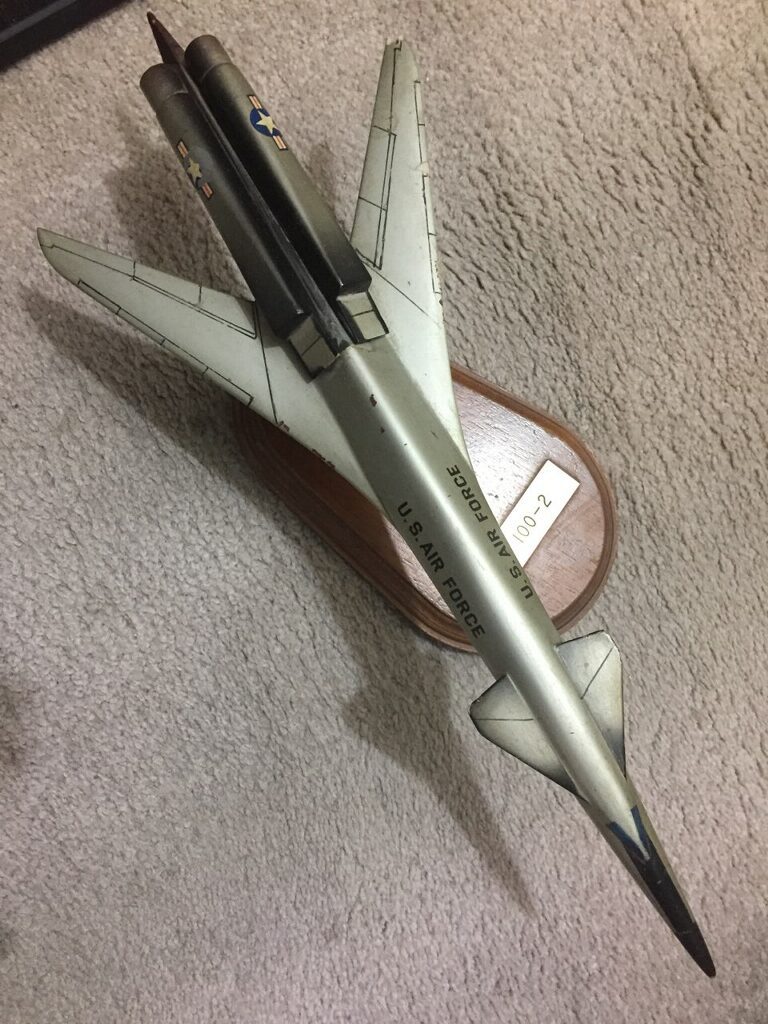
A little while back I was contacted by someone who had an old display model of a Boeing Controlled Configured Vehicle bomber and wondered if I was interested in buying it. Interested? Yes. Able? No. But I was able to put the seller in contact with someone else who was able to procure it, so this Boeing CCV-100-2 wound up in a good home. More on the CCV-100-2 is HERE. Still no confirmation of the scale of the vehicle, sadly.
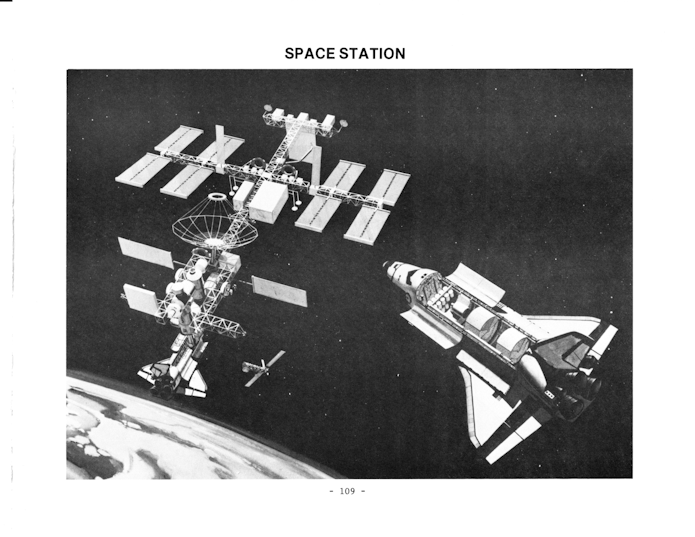
In 1985, Rockwell International contemplated the idea of the Space Station turning a profit for the company. At this point the Space Station seemed a reasonably certain program, though it would take another decade, the fall of the USSR and several complete revamps before assembly would really begin .
Next: advanced manned military spacecraft.
Air Force Displays Model Of Exotic And Potentially Revolutionary Hybrid Electric Airlifter
@AFResearchLab unveiled novel distributed propulsion concept vehicle at #aiaaSciTech – incorporating array of electric fans could be basis for ‘vision vehicle’ for future @usairforce STOL tactical airlifter pic.twitter.com/UXfdrehXr7
— Guy Norris (@AvWeekGuy) January 8, 2020
The propulsion system may be efficient, but it has the appearance of not being a particularly stealthy one, which makes for a schizophrenic contrast with the clearly stealthified fuselage. Amusingly, if you look closely the USAF insignia on the wings of the model are *deeply* engraved.
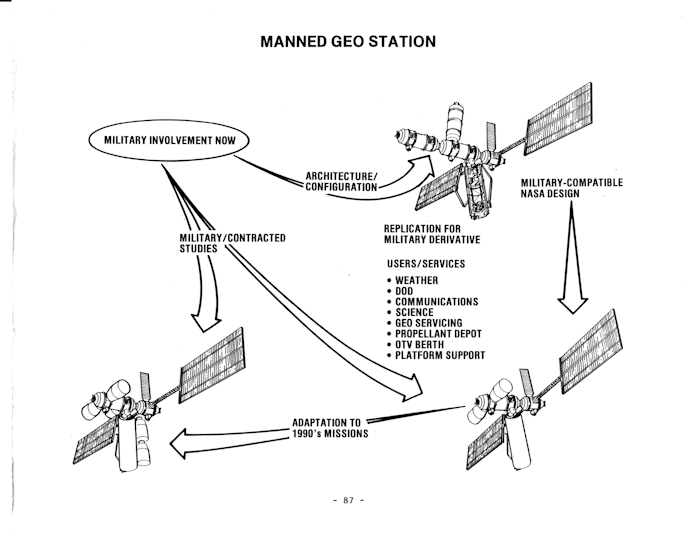
In 1985 Rockwell – perhaps half-heartedly – suggested the possibility of a business case for a manned station in geosynchronous orbit. The station would be used to service satellites in GEO. While an interesting notion, satellites in GEO relatively rarely require any actual servicing; the three billion dollars Rockwell expected such a system would cost (and let’s face it, the cost would doubtless balloon) would likely far outweigh the cost of simply replacing the satellites.