From 1965, two Boeing-Vertol Heavy Lift Helicopter concepts in model form, to scale with a Chinook (at far right). At far left is the Model 227 which carried loaded internally; in the middle is Model 237, designed as a flying crane. note, though, that even though the Model 237 is designed to carry payloads externally the vehicle is so large that the reduced fuselage still has room for a substantial passenger load, windows and all.
One of the main purposes of the Monthly Historical Documents Program/APR Patreon is to get rare aerospace items from eBay. These items are then made available to subscribers/patrons via monthly votes and catalogs.
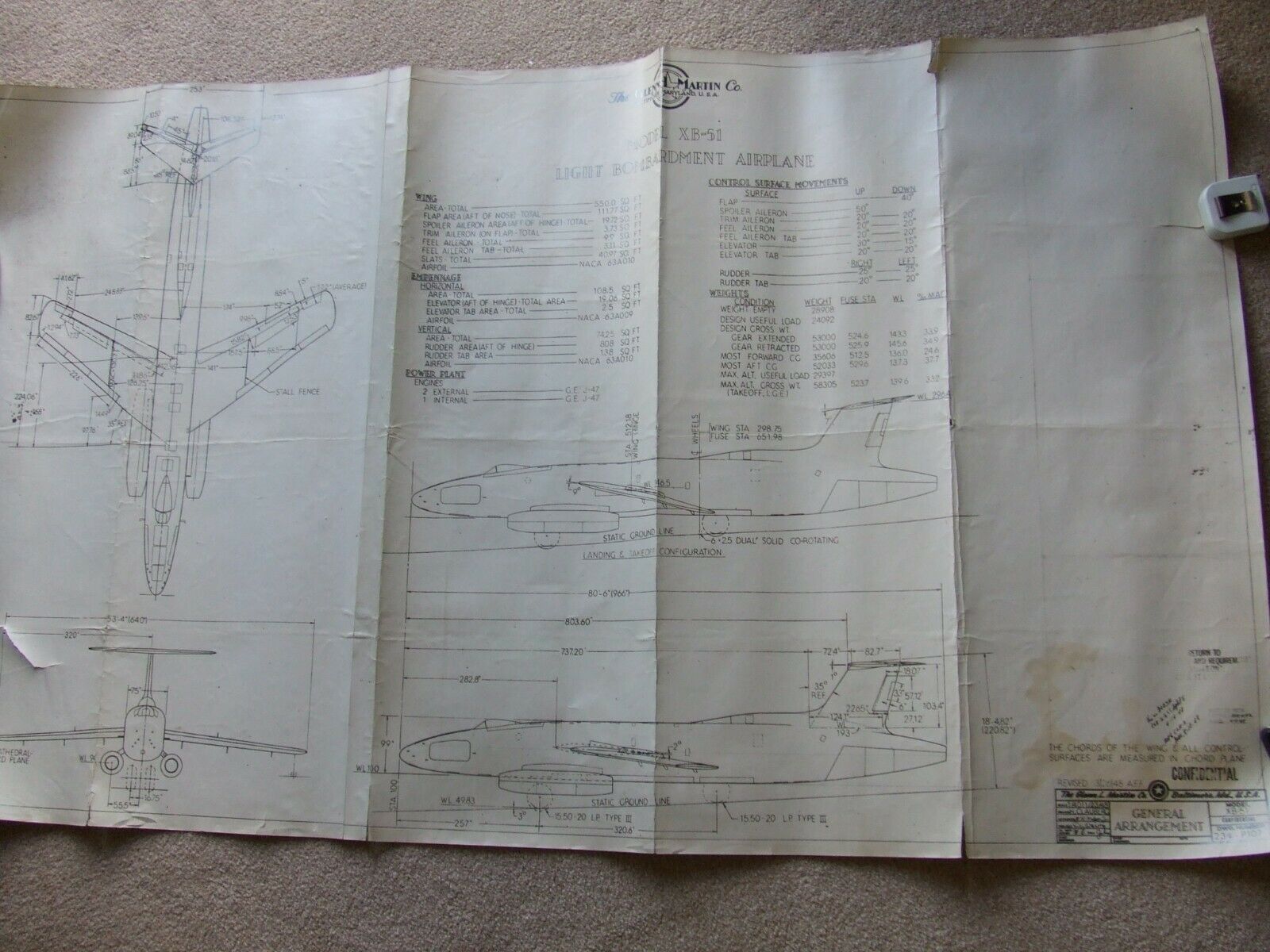
Below are some of the items I’ve recently paid for (though not as yet received). If you are interested in getting high-rez scans and/or helping me save these sort of things for future generations (as well as keeping my cats in food and litter), please consider signing up for the Monthly Historical Documents Program or the APR Patreon.
Virgin Galactic Unveils Mach 3 Aircraft Design for High Speed Travel, and Signs Memorandum of Understanding with Rolls-Royce
Similar in layout to Concorde. Doubtless similar issues in making it make any sort of economic sense.



Not much in the way of details (Mach 3 cruise above 60,000 feet), and the artwork is very likely essentially speculative. Passenger count is a meager 9 to 19, putting it squarely in the “business jet” category.
Fantastic plastic has recently released some model kits that I created the CAD models for:
Northrop Low Altitude Penetrator:
“Razorback” from “The Expanse,” to the same scale with the earlier “Rocinante:”
Northrop M2F3 in 1/48 scale:
Some earlier FP models that might be of interest:
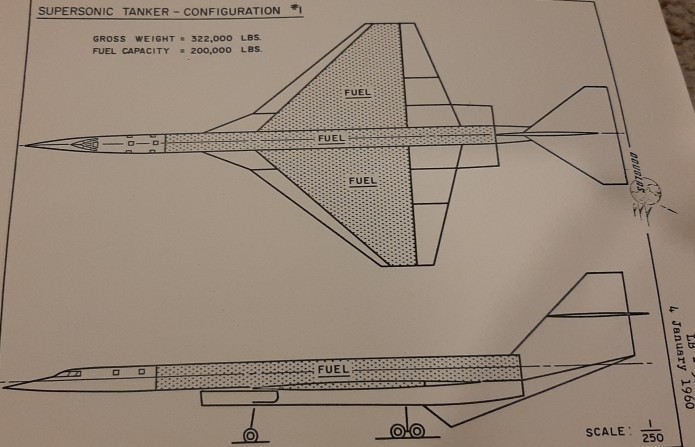
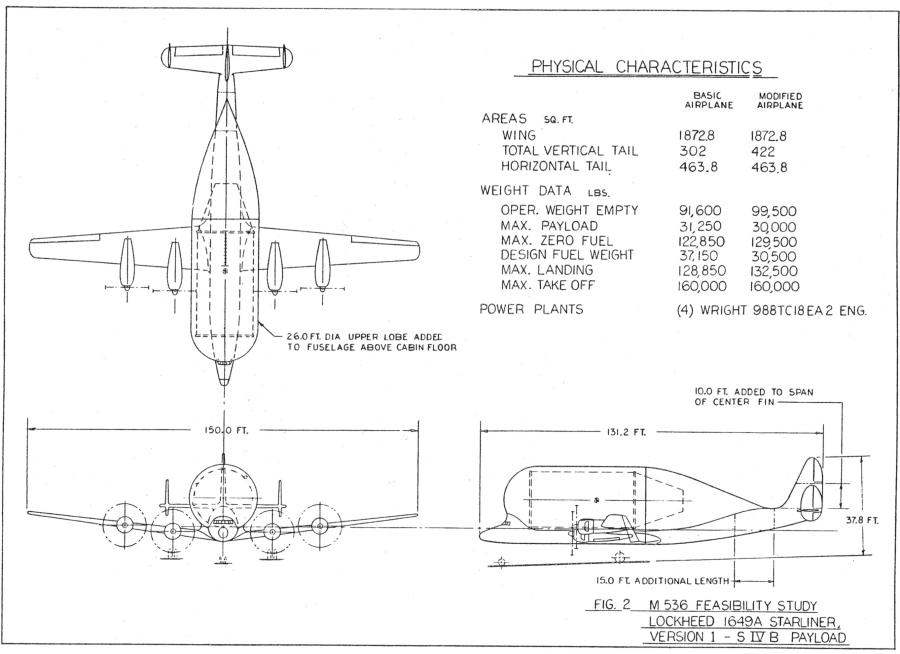
In 1964 Fairchild Stratos pitched a number of concepts for converting aircraft into carriers for Saturn rocket stages. One idea was a highly modified Convair B-36; this concept was illustrated in US Transport Projects #4, available HERE. Another was to convert a Lockheed Starliner, the final form of the venerable Constellation line of passenger airliner. This was not as massively modified as the B-36. Here, the Fairchild M-536 had a large aerodynamic “pod” was added to the top that would fit a S-IV stage. The fuselage was lengthened by 15 feet and the central vertical stabilizer was extended.
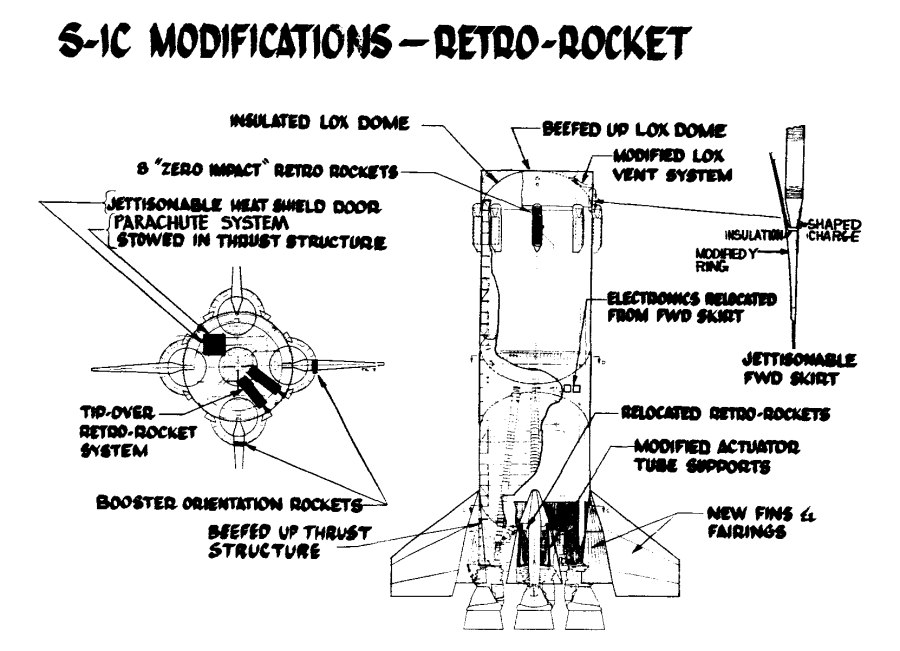
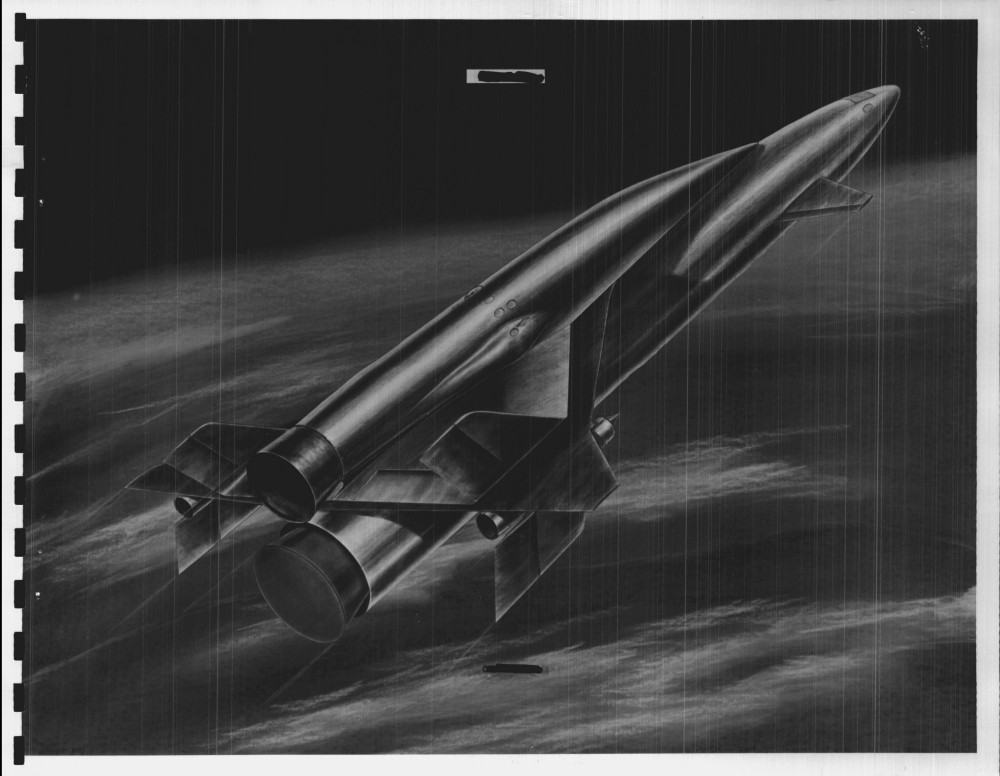
An illustration from a 1964 Boeing report on Saturn V first stage recovery and re-use. A number of concepts were studied, from balloons to parachutes. This particular one used parachutes to slow the stage and solid propellant retro-rockets in the nose for terminal braking, doing something akin to Falcon’s “hoverslam” just before splashdown. The forward LOX dome in the concept would be structurally strengthened to survive the impact. After the initial splash, rockets would be used to tip the stage over in a particular direction… and then more, bigger rockets would be used just before the stage fell over to keep it from hitting too hard.
Another concept was to use a design that would blow off the LOX tank forward dome before impact. The stage would thus hit the water like an inverted cup. As the water compressed the air within the LOX tank, blowout doors at the “bottom” of the tank would, well, blow out, giving the compressed air somewhere to go. This would serve as a pneumatic shock absorber for the stage, but it would pretty much trash the LOX tank.
In 1963-64, NASA was looking forward to a very bright future. Moon landings within a handful of years, a serious space station or two in the early seventies, manned missions to the vicinity of Mars and/or Venus probably by the early eighties, manned Mars landings not long after. Moon bases, Mars based, nuclear rockets, missions to the asteroids and the moons of Jupiter… in 1964, the rest of the 20th century must’ve looked *fantastic.*
In order to pull all that off, it was clear that NASA would need to launch a *lot* of astronauts. Consequently, a request for proposals went out to the aerospace industry to design the capability to do just that. Boeing, North American, Martin, Lockheed… a great deal of interest was shown and work accomplished. One design produced is illustrated below, a Lockheed design for a two-stage fully reusable spaceplane capable of transporting ten tons of payload or ten passengers to an orbiting space station. The booster stage had a cockpit about where you’d expect; the spaceplane, conversely, had an offset spaceplane so that the crew would have *some* sort of forward view during landing. Both stages used advanced rocket engines; the first stage also had turbojets to get it back to the launch site. As with all pre-Shuttle designs, estimates of turnaround time and minimal launch cost are impressive and a bit depressing in just how fabulously optimistic they were.
An earlier three-stage concept was shown in US Launcher Projects #5.
The future looked bright. And then… LBJ.
Several recommendations have come in over the years to set up an APR Discord server… which has now been done. I’m still in the process of configuring it and figuring it all out, but once it’s up and running it will serve as sort of a backup to the APR blog. It is something that seems to be available solely via invitation, so there will be some other little features it’ll have… such as, probably, even more restricted discussion forums specifically about Book 1 and Book 2 (“Book X” and “Book XX,” whatever) where I will describe them and post preview images such as representative diagrams, lists of vehicles to be illustrated, possibly early stabs at cover art, etc.
Subscribers to the APR Patreon and the Monthly Historical Documentation Program will all get invites when the time comes. I’m thinking of inviting the higher-level patrons/subscribers into the Book1 & 2 subforums. At the moment it’s pretty bare… there are channels for “Aircraft projects,” “spacecraft projects,” “aerospace news,” “aircraft – built” (as opposed to “projects), “general” (which is just for discussion of the APR Discord server itself) and “US Aerospace Projects,” which will go into further detail about the USxP issues I’ve released and plan to release.
If anyone has experience with such things, feel free to leave recommendations and suggestions in the comments.